Andrew Innerarity / California Department of Water Resources.
Water, water, every where, nor any drop to drink.
— Samuel Taylor Coleridge’s poem The Rime of the Ancient Mariner.
Desalination, the process of turning seawater into potable water, is gaining traction as a viable solution to California’s perennial drought issues. The Golden State, with its sprawling 850-mile coastline and notorious aridity, is primed for desalination to play a pivotal role in its water management strategies.

California’s history with droughts is long and storied, with the state experiencing some of its driest years on record recently. Traditional sources of water, such as snowpacks and reservoirs, have become increasingly unreliable due to the erratic patterns of climate change. While an atmospheric river storm in 2023 and several powerful storms in 2024 and 2025 significantly eased California’s drought conditions for the time being, there is widespread concern that serious drought conditions will soon return and become the new norm.
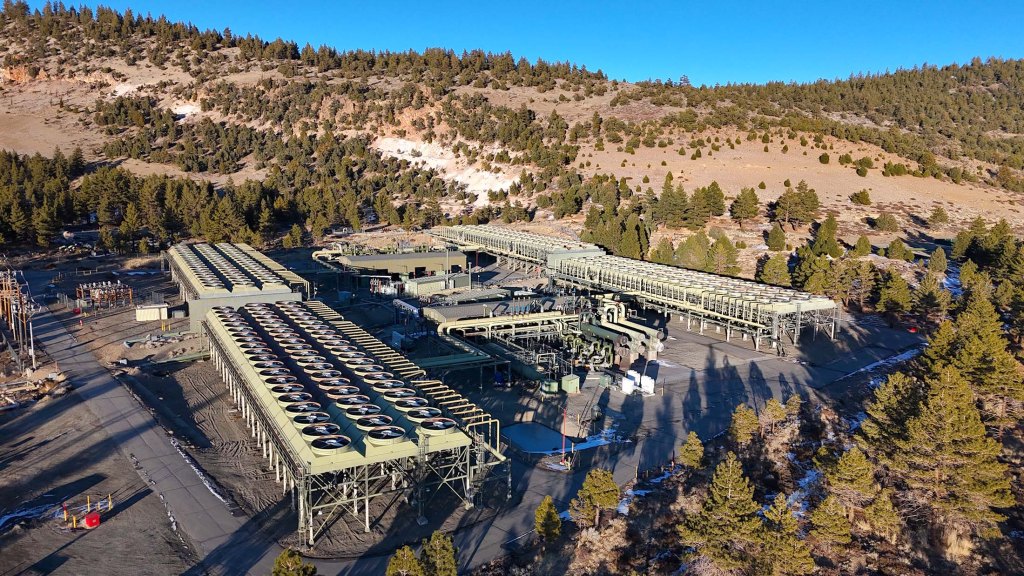
As a response, several desalination plants have emerged along the coast. One notable example is the Claude “Bud” Lewis Carlsbad Desalination Plant in San Diego County, which is the largest in the Western Hemisphere, providing about 50 million gallons of drinking water daily.
Every day, 100 million gallons of seawater pass through semi-permeable membranes, producing 50 million gallons of fresh water delivered directly to municipal users. The Carlsbad plant, which has been fully operational since 2015, now provides roughly 10 percent of the freshwater supply used by the region’s 3.1 million residents—although at nearly double the cost of water from the region’s primary alternative sources.

Desalination is not just a process but a symphony of advanced technologies working in concert. The most prevalent method used in California is reverse osmosis (RO). RO employs a semi-permeable membrane that allows water molecules to pass through while blocking salt and other impurities. This membrane is the linchpin of the operation, designed to withstand the high pressures necessary to reverse the natural process of osmosis where normally, water would move from a low-solute concentration to a high-solute concentration.

CALIFORNIA CURATED ART ON ETSY
Purchase stunning mugs and art prints of iconic California scenes.
Check out our Etsy store.
Reverse osmosis desalination is an energy-intensive process, one that demands a significant amount of power to be effective. At its core, the technique involves forcing seawater through a semi-permeable membrane to separate salt and other minerals, yielding fresh water. This process, however, requires substantial pressure, much higher than the natural osmotic pressure of seawater, to push the water through the membrane. Achieving and maintaining this pressure consumes a considerable amount of energy. Furthermore, the energy demands are compounded by the need for constant system maintenance and the treatment of the highly saline brine that’s left over. This energy requirement is a key challenge in making reverse osmosis desalination a more widespread solution for water scarcity, as it not only increases operational costs but also has environmental implications, especially if the energy comes from non-renewable sources.

The science behind these membranes is fascinating. They are not just filters; they are engineered at the molecular level. The membranes are typically made from polyamide, created through complex chemical reactions that result in a thin film where the magic happens. Water molecules navigate through this film via tiny pores, leaving behind salts and minerals.
This scientific marvel, however, has additional environmental challenges. Along with the vast energy needs of reverse osmosis, there are also concerns about water pollution. Brine, which is the concentrated saltwater byproduct, must be carefully managed to avoid harming marine ecosystems when it’s discharged back into the ocean.

Innovations continue to improve the technology, aiming to make desalination more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. New approaches such as forward osmosis, which uses a natural osmotic pressure difference rather than mechanical pressure, and the use of alternative energies like solar and wind power are on the horizon. There’s also ongoing research into biomimetic membranes, inspired by nature’s own filtration systems, such as those found in the roots of mangrove trees or in the kidneys of animals.
In addition to the sprawling, successful desalination plant in Carlsbad, numerous other projects are on the way. The Doheny Ocean Desalination Project, located in Dana Point, has seen a significant increase in projected costs but is still moving forward. It’s expected to be completed by 2027 and will provide about 5 million gallons of drinking water daily to residents in Orange County.
In November, the California Coastal Commission greenlit a permit for the Monterey Bay Area Desalination Plant, a vast $330 million seawater desalination plant in Marina, a modest city of 22,500 people located roughly 15 minutes north of the more prosperous Monterey. The proposed Cal-Am desalination facility, if finalized, is set to produce 4.8 million gallons of fresh water daily.

However, Marina’s Mayor, Bruce Delgado, stands in opposition to the project. He argues that it would alter the character of Marina and negatively impact its natural surroundings. Delgado contends that while his city would shoulder the environmental and industrial impacts of the plant, the adjacent, wealthier areas such as Carmel-by-the-Sea, Pacific Grove, and Pebble Beach would enjoy most of the benefits.
In February 2024, the California Department of Water Resources (DWR) released a report identifying future brackish water desalination projects to enhance the state’s water reliability. The report aims to meet goals outlined in California’s Water Supply Strategy: Adapting to a Hotter, Drier Future, which targets increasing water supply by implementing new brackish desalination projects providing 28,000 acre-feet per year by 2030 and 84,000 acre-feet per year by 2040.

As California looks to the future, the role of desalination is poised to expand. The state’s water plan includes the potential for more desalination facilities, particularly in coastal cities that are most affected by drought and have direct access to the sea. The integration of desalination technology with California’s complex water infrastructure speaks to a broader trend of marrying innovation with necessity.
The implications for drought-prone regions extend beyond just survival; they encompass the sustainability of ecosystems, economies, and communities. While desalination is not a panacea for all of California’s water woes, it represents a critical piece of the puzzle in the quest for water security in an era of uncertainty. As the technology advances, it may well become a cornerstone of how humanity adapts to a changing climate, making what was once undrinkable, a wellspring of life.