When we step outside and see wildlife, we often think of it as unchanging. A bird on a branch, a crab in a tide pool, a lizard skittering across a sidewalk. It feels timeless. But in truth, these animals are evolving, slowly and steadily, right in front of us. As climates become more unpredictable, habitats shift, food sources change, and nature adapts. This is especially true in our cities. Built over just the past few centuries, these sprawling human environments are reshaping the natural world and pushing wildlife to adjust in new and often surprising ways.
As California’s cities have expanded and encroached upon natural landscapes, it turns out the state’s wildlife is adapting in fascinating ways. Studying these changes is central to urban evolution, or how species adapt over time, both genetically and behaviorally, to the unique pressures of city life. From coyotes navigating traffic to birds adjusting their songs to be heard over city noise, urban evolution reveals how nature is not just surviving in cities, but evolving with them. Darwin believed natural selection was too slow to observe in real time, but today we know evolution can happen rapidly, sometimes within just a few generations.
Thanks for reading California Curated Newsletter! Subscribe for free to receive new posts and support my work.
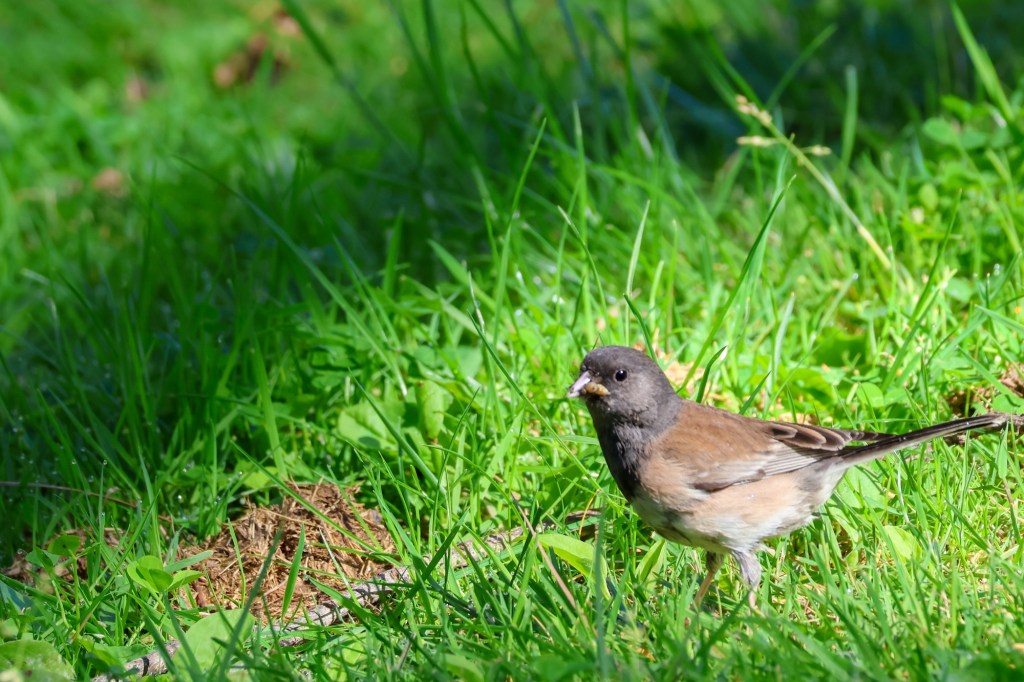

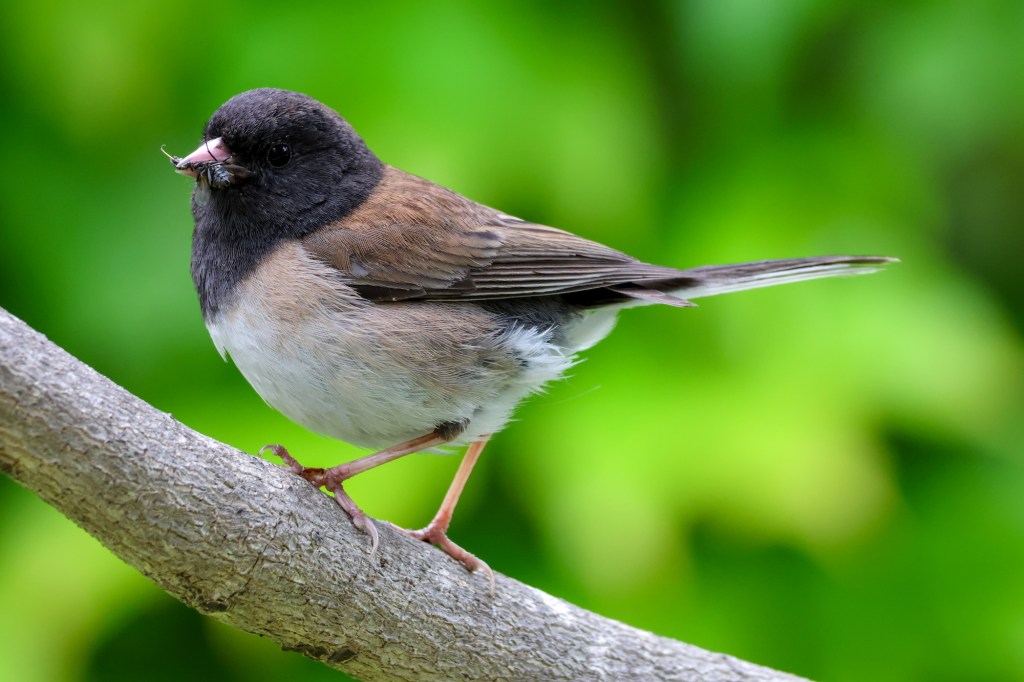
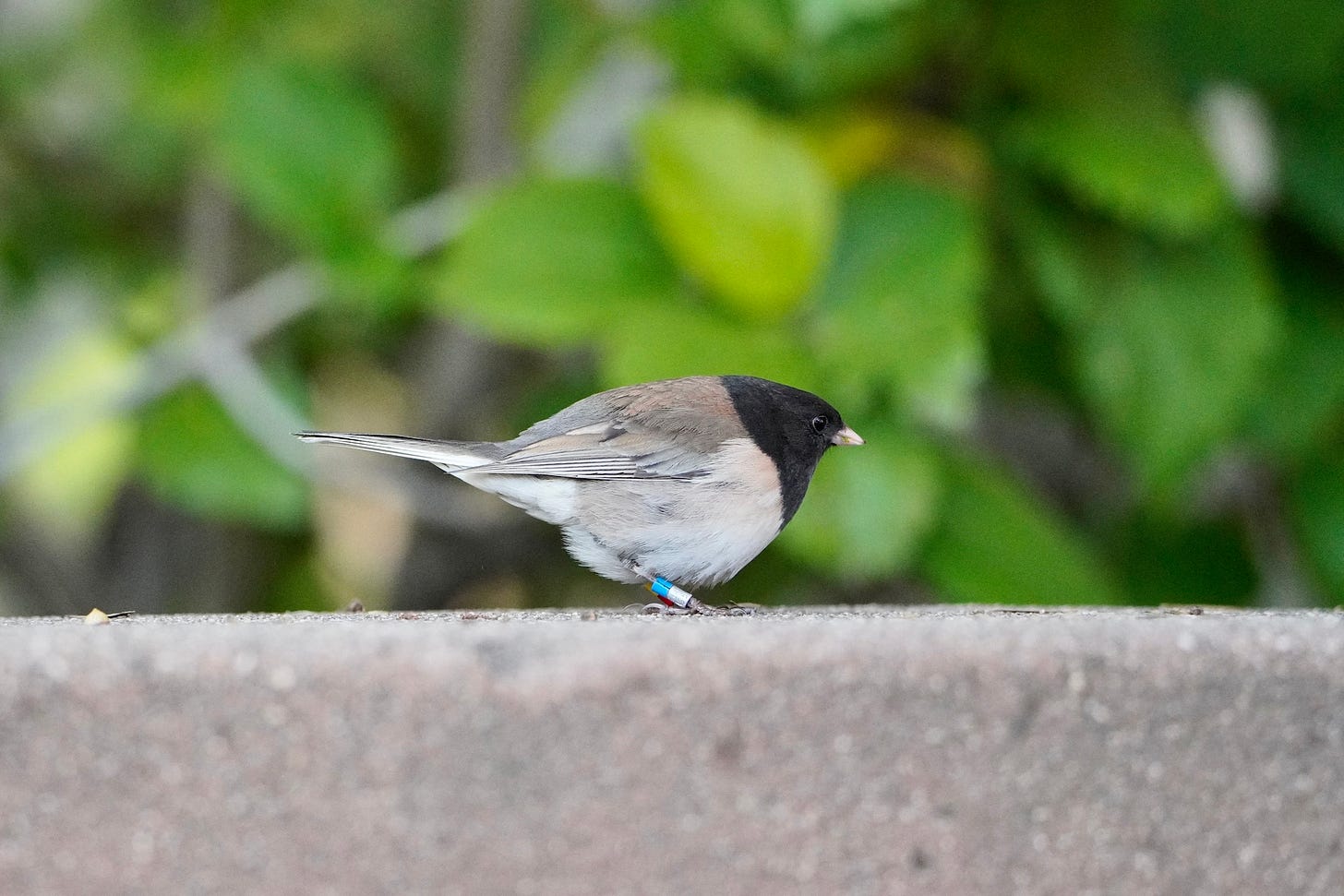
One cool example of urban evolution in California is the story of the dark-eyed junco (Junco hyemalis), a small songbird traditionally found in mountainous forests that is now thriving in urban environments like San Diego and Los Angeles. If you’re a birder or simply someone who enjoys watching the wildlife in your backyard, you’ve almost certainly seen them. Dark-eyed juncos are small songbirds with distinctive dark heads, often spotted hopping around on the ground rather than perching at feeders. I see them all the time, pecking at the spilled seeds beneath my feeder (or, I should say feeders, as I have several…nerd alert!). It turns out they’re classic ground foragers, evolved to search for food by scratching through leaf litter or snow, uncovering seeds, insects, and other hidden bits.
Recent research has revealed that dark-eyed juncos are evolving in direct response to urban life. Traditionally migratory, these birds once spent summers breeding in cool mountain forests and winters at lower elevations. But in the early 1980s, a group of juncos broke from that pattern and settled year-round on the campus of UC San Diego. There, researchers began documenting striking behavioral shifts. The urban juncos were bolder, less fearful of humans, and had even altered their mating and nesting habits. These changes, observed over just a few decades, offer a vivid example of how quickly species can adapt to city environments, a real-time case study in urban evolution unfolding in human-shaped habitats.

Similarly, at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), a junco population has been thriving for decades, with numbers reaching approximately 300. This long-term success has provided the Yeh Lab at UCLA with a unique opportunity to study how urban environments influence the evolution and behavior of these adaptable songbirds. Their research sheds light on how juncos have adjusted to city life, offering broader insights into wildlife resilience in human-altered habitats.
“It’s impressive how rapidly these vertebrate species can evolve. In a matter of a handful of years, we can find some pretty significant changes,” Pamela Yeh, an associate professor in ecology and evolutionary biology at UCLA, told California Curated. Yeh studied the junco population at UC San Diego when she was an undergraduate student there and wanted to expand the research to the population at UCLA. Studying the two different populations may offer insights into how species evolve in urban environments.
“We want to know, does a city make you evolve?” asks Yeh. “Do the different cities make you evolve similarly? Do the birds all become smaller? Do they all become bigger? Do they all have different-sized beaks? Or is each city unique?”

With decades of data, the work echoes the groundbreaking research of Princeton scientists Peter and Rosemary Grant, whose studies of Galápagos finches transformed our understanding of how swiftly natural selection can operate. Now, the junco studies are taking that idea further, showing evolution unfolding not on remote islands, but in the heart of our cities.
“I think it’s now really considered a model vertebrate system for urban evolution,” says Yeh.
In their natural forest environments, juncos breed in response to the changing seasons, triggered by increasing daylight hours and rising temperatures. But in urban areas like those around UCSD and UCLA, where food is plentiful year-round, juncos have begun breeding earlier than normal and throughout the year. They build nests higher off the ground, often on artificial structures, and have increased the number of clutches per breeding season. The availability of artificial light, abundant food from human sources, and fewer natural predators in the city all play roles in these behavioral shifts.
Yeh believes it’s no accident that junco populations have surged on college campuses in recent decades. In fact, she sees it as a direct response to the unique conditions these urban environments provide.

“We think it is is partially that [urban university environments] mimic the natural environment, which is a mix of meadows and tall trees. But the other thing that we think could be important is the irrigation in grassy areas that allow the juncos, even when it’s extremely hot, there are still small insects and worms to grab and feed their offspring.”
One of the most striking adaptations among urban juncos is their behavioral shift in regards to people. Unlike their shy mountain counterparts, urban juncos are much more tolerant of human presence. This is not only a matter of convenience; it’s a survival mechanism. In the city, humans are not a threat, and urban birds need to capitalize on the resources provided by their proximity to people. Their lack of fear “allows them to keep eating even when we walk by,” says Yeh.
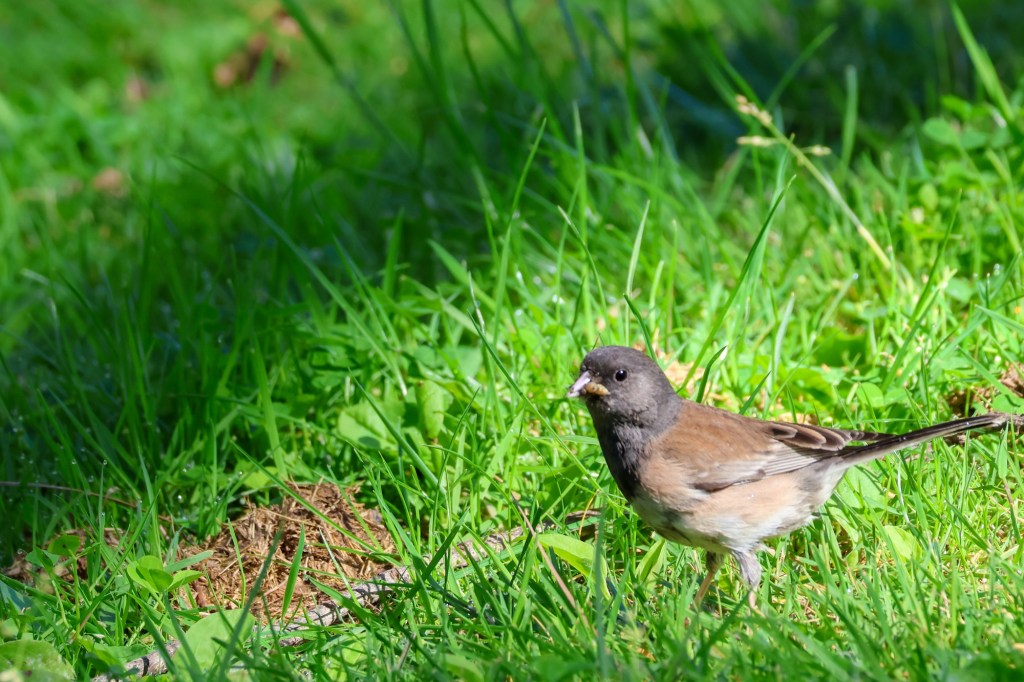

Studying junco evolution isn’t just a scientific curiosity. It has real conservation stakes. Things haven’t been looking good for birds. An October 2019 study published in Science by the Cornell Lab of Ornithology revealed that North America has lost nearly 3 billion birds over the past 50 years, with dark-eyed juncos alone declining by 168 million. Yet their ability to adapt to urban life suggests they may have the evolutionary tools needed to weather these dramatic changes.
Beyond behavior, there are physical differences between urban and rural populations of dark-eyed juncos. Urban juncos, for example, developed duller black plumage on their heads and showed reduced white markings in their tail feathers. Yeh and her team have also documented that the wings of urban juncos are smaller, an adaptation likely driven by the demands of maneuvering through a dense, built environment rather than long-distance flight.
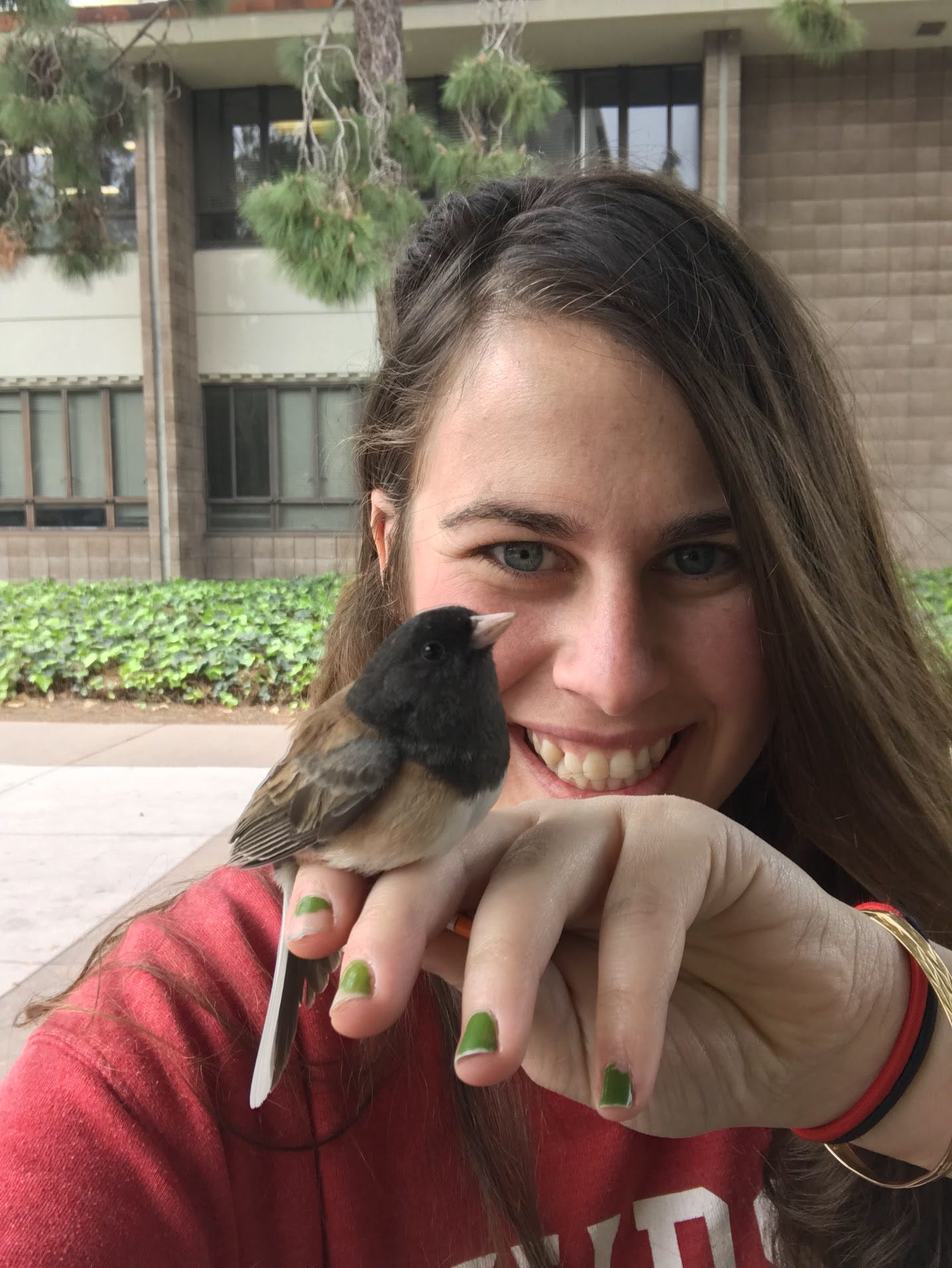

“Juncos historically were migratory birds. The ones that live in the mountains still are. But in the urban environments, we see them year-round,” says Dr. Ellie Diamant, Visiting Assistant Professor at Bard College. “So the benefits are gone for the longer-distance flight, but there seems to be more benefit for these short wings.” Diamant completed her Ph.D. in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at UCLA in the Yeh Lab.
The dark-eyed junco is just one example of the broader phenomenon of urban evolution, where species adjust to the challenges and opportunities posed by city life. In California, this phenomenon extends beyond birds. Coyotes, for example, have become fixtures in cities like Los Angeles, adapting to scavenge food from human waste. Coastal animals like sea lions and pelicans have also made urban waterfronts their home, thriving amid the bustle of human activity. Similarly, the Western Fence Lizard has swiftly adapted to life in an urbanized environment.

In his book Darwin Comes to Town, Dutch evolutionary biologist Menno Schilthuizen highlights the junco as an exemplar of rapid evolution in urban settings, but it also goes much further, documenting how our manmade environments are accelerating and changing the evolution of the animals and plants around us. Of course, it’s not all good news. Not by a long shot.
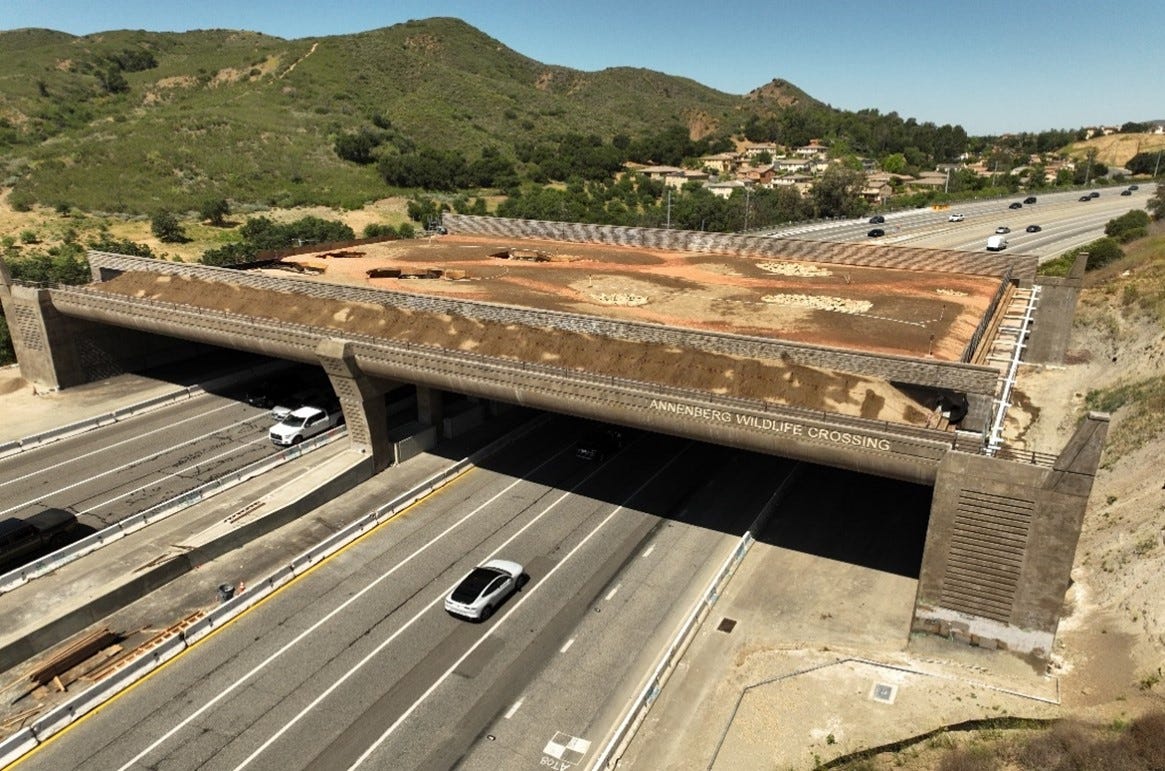
Studies published in Evolutionary Applications, underscore that urbanization is a double-edged sword, offering opportunities for adaptation but also introducing serious threats. In Los Angeles, for instance, the fragmentation of habitat by highways has led to the deaths of countless animals, a problem now being tackled through the construction of wildlife bridges like the Wallis Annenberg Wildlife Crossing opening in 2026, designed to reconnect critical migration routes.

The dark-eyed junco’s ability to adapt to city life is both encouraging and a bit sobering. It shows how some wildlife can adjust and find ways to thrive even as human development spreads. But it also reflects the growing pressure we’re putting on natural ecosystems. In other words, it’s not all good, and it’s not all bad. As scientists dig deeper into urban ecology in California and elsewhere, the junco stands out as a clear example of how life shifts and changes in response to the world we’re shaping.
For those of us who live in cities, the juncos flitting through parks, pecking in our yards, and hopping across college campuses offer a chance to see evolution happening right in front of us. Nature isn’t some distant thing beyond the city limits. It’s here, threaded into the daily patterns of urban life.