I love reading New York Times obituaries, not because of any morbid fascination with death, but because they offer a window into extraordinary lives that might otherwise go unnoticed. These tributes often highlight people whose work had real impact, even if their names were never widely known. Unlike the celebrity coverage that fills so much of the media, these obituaries can be quietly riveting, full of depth, insight, and genuine accomplishment.
For two years I managed the New York Times video obituary series called Last Word. We interviewed people of high accomplishment who had made a difference in the world BEFORE they died, thus giving them a chance, at a latter age (in our case 75 was the youngest, but more often people would be in their 80s) to tell their own stories about their lives. They signed an agreement acknowledging that the interview would not be shown until after their death. Hence the series title: Last Word. Anyway, when I ran the program, I produced video obituaries for people as varied as Neil Simon, Hugh Hefner, Sandra Day O’Connor, Philip Roth, Edward Albee, and my favorite, the great Harvard biologist E.O. Wilson. Spending time and learning about their lives in their own words was a joy.
All of that is to say that obituaries often reveal the lives and accomplishments of people who have changed the world. These are stories that might never be told so thoughtfully or thoroughly anywhere else.
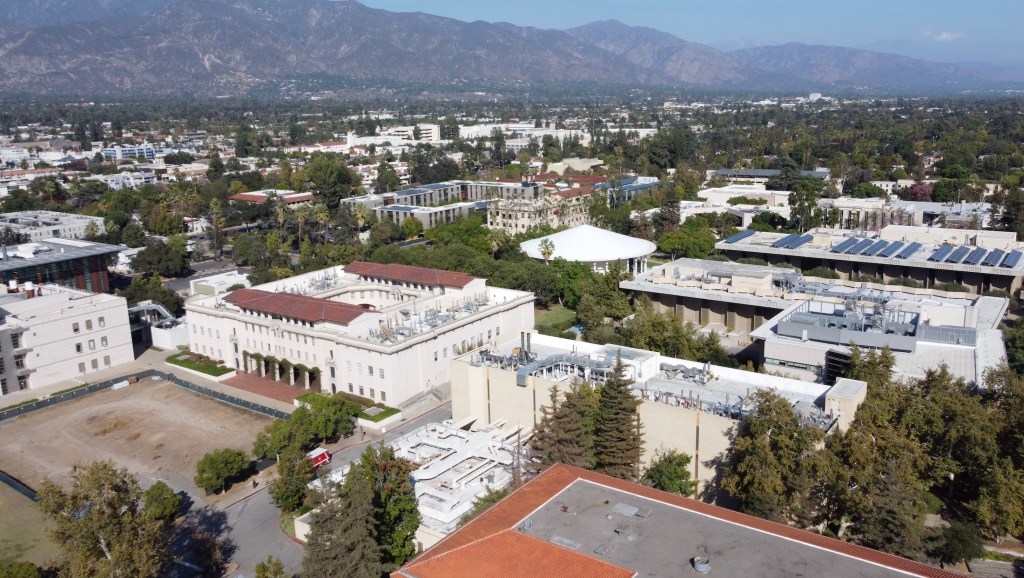

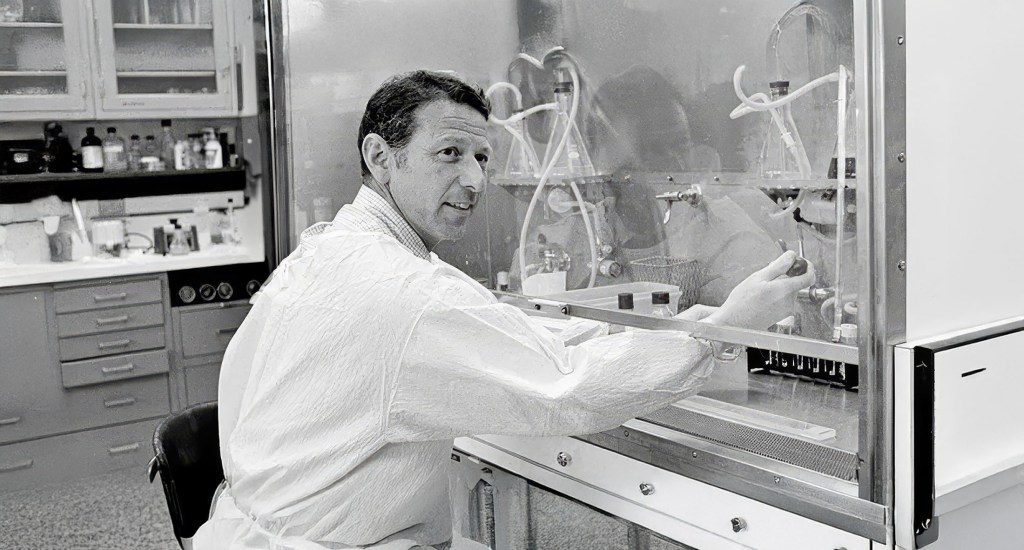
Which bring us to a quiet lab at Caltech in 1958, where two young biologists performed what some still call “the most beautiful experiment in biology”. Their names were Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl, and what they uncovered helped confirm the foundational model of modern genetics. With a simple centrifuge, a dash of heavy nitrogen, and a bold hypothesis, they confirmed how DNA, life’s instruction manual, copies itself. And all of it took place right here in California at one of the world’s preeminent scientific institutions: the California Institute of Technology or CalTech, in Pasadena. The state is blessed to have so many great scientific minds and institutions where people work intensely, often in obscurity, to uncover the secrets of life and the universe.

Franklin Stahl died recently at his home in Oregon, where he had spent much of his career teaching and researching genetics. The New York Times obituary offered a thoughtful account of his life and work, capturing his contributions to science with typical respect. But after reading it, I realized I still didn’t fully grasp the experiment that made him famous, the Meselson-Stahl experiment, the one he conducted with Matthew Meselson at Caltech. It was mentioned, of course, but not explained in a way that brought its brilliance to life. So I decided to dig a little deeper.

The Meselson-Stahl experiment didn’t just prove a point. It told a story about how knowledge is built: carefully, creatively, and with a precision that leaves no room for doubt. It became a model for how science can answer big questions with simple, clean logic and careful experimentation. And it all happened in California.
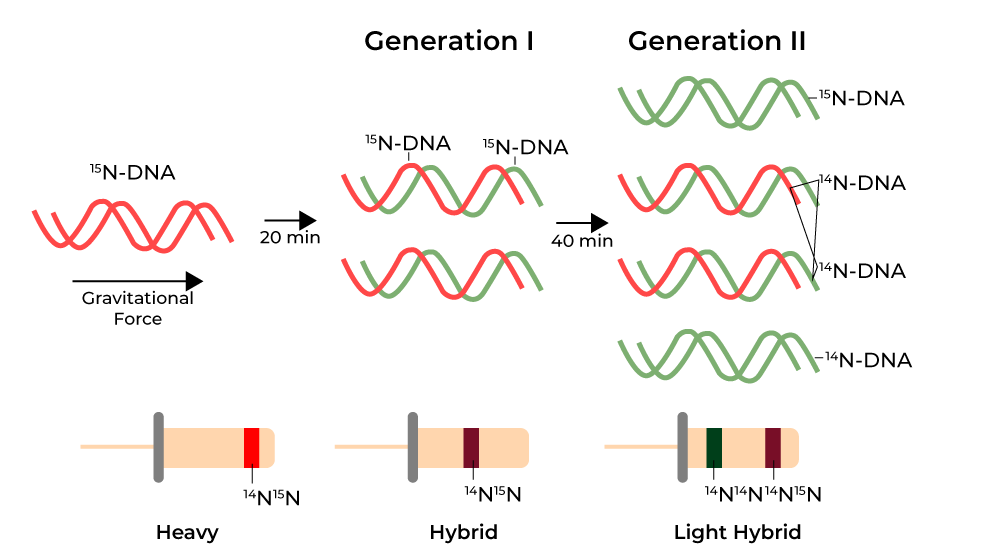
Let’s back up: When Watson and Crick proposed their now-famous double helix structure of DNA in 1953 (with significant, poorly recognized help from Rosalind Franklin), they also suggested a theory about how it might replicate. Their idea was that DNA separates into two strands, and each strand acts as a template to build a new one. That would mean each new DNA molecule is made of one old strand and one new. It was called the semi-conservative model. But there were other theories too. One proposed that the entire double helix stayed together and served as a model for building an entirely new molecule, leaving the original untouched. Another suggested that DNA might break apart and reassemble in fragments, mixing old and new in chunks. These were all plausible ideas. But only one could be true.
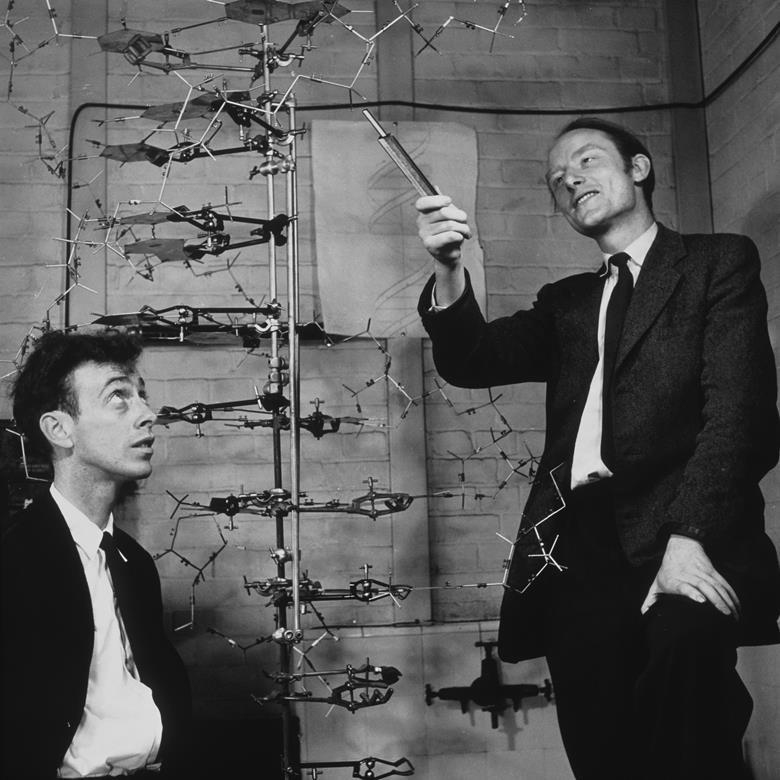

To find out, Meselson and Stahl grew E. coli bacteria in a medium containing heavy nitrogen (nitrogen is a key component of DNA), a stable isotope that made the DNA denser than normal. After several generations, all the bacterial DNA was fully “heavy.” Then they transferred the bacteria into a medium with normal nitrogen and let them divide. After one generation, they spun the DNA in a centrifuge that separated it by weight. If DNA copied itself conservatively, the centrifuge would show two bands: one heavy, one light. If it was semi-conservative, it would show a single band at an intermediate weight. When they performed the experiment, the result was clear. There was only one band, right between the two expected extremes. One generation later, the DNA split into two bands: one light, one intermediate. The semi-conservative model was correct.
Their results were published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences in 1958 and sent shockwaves through the biological sciences.
To me, the experiment brought to mind the work of Gregor Mendel, an Augustinian monk who, in the mid-1800s, quietly conducted his experiments in the garden of a monastery in Brno, now part of the Czech Republic. By breeding pea plants and meticulously tracking their traits over generations, Mendel discovered the basic principles of heredity, dominant and recessive traits, segregation, and independent assortment, decades before the word “gene” even existed. Like Mendel’s experiments, the Meselson-Stahl study was striking in its simplicity and clarity. Mendel revealed the rules; Meselson and Stahl uncovered the mechanism.
There’s a fantastic video where the two men discuss the experiment that is worth watching. It was produced produced by iBiology, part of the nonprofit Science Communication Lab in Berkeley. In it Meselson remembered how the intellectual climate of CalTech at the time was one of taking bold steps, not with the idea of making a profit, but for the sheer joy of discovery: “We could do whatever we wanted,” he says. “It was very unusual for such young guys to do such an important experiment.”

Most people think of Caltech as a temple of physics. It’s where Einstein lectured, where the Jet Propulsion Laboratory was born (CalTech still runs it), and where the gravitational waves that rippled through spacetime were detected. But Caltech has a quieter legacy in biology. Its biologists were among the first to take on the structure and function of molecules inside cells. The institute helped shape molecular biology as a new discipline at a time when biology was still often considered a descriptive science. Long before Silicon Valley made biotech a household term, breakthroughs in genetics and neurobiology were already happening in Southern California.
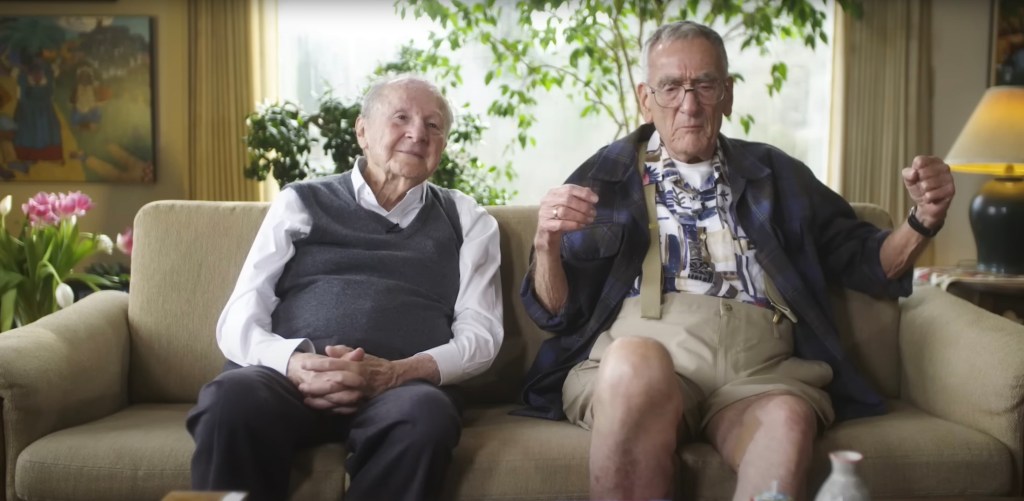

The Meselson-Stahl experiment is still taught in biology classrooms (my high school age daughter knew of it) because of how perfectly it answered the question it set out to ask. It was elegant, efficient, and unmistakably clear. And it showed how a well-constructed experiment can illuminate a fundamental truth. Their discovery laid the groundwork for everything from cancer research to forensic DNA analysis to CRISPR gene editing. Any time a scientist edits a gene or maps a mutation, they are relying on that basic understanding of how DNA replicates.
In a time when science often feels far too complex, messy, or inaccessible, the Meselson-Stahl experiment is a reminder that some of the most important discoveries are also the simplest. Think Occam’s Razor. Two young scientists, some nitrogen, a centrifuge, a clever idea, and a result that changed biology forever.








