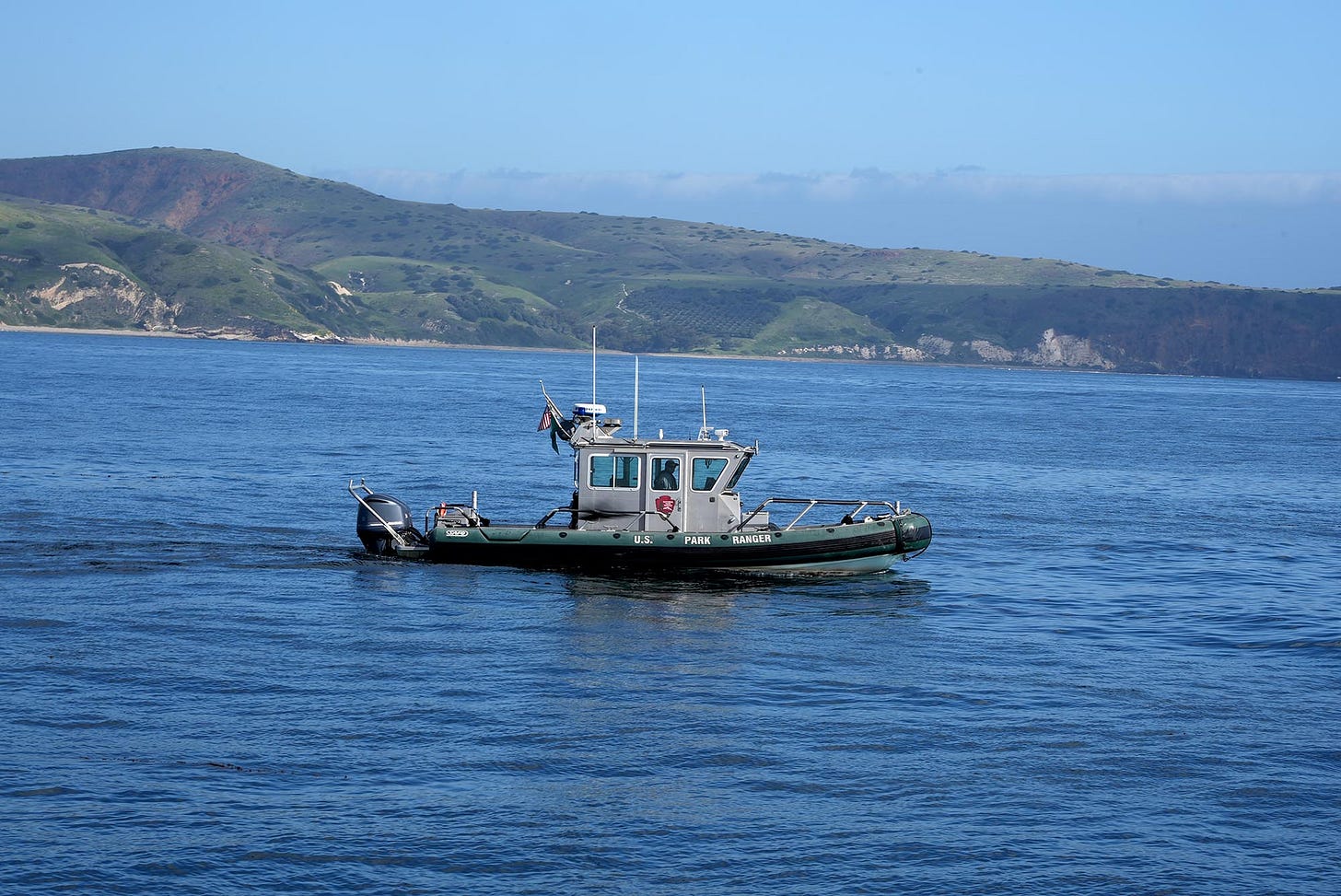
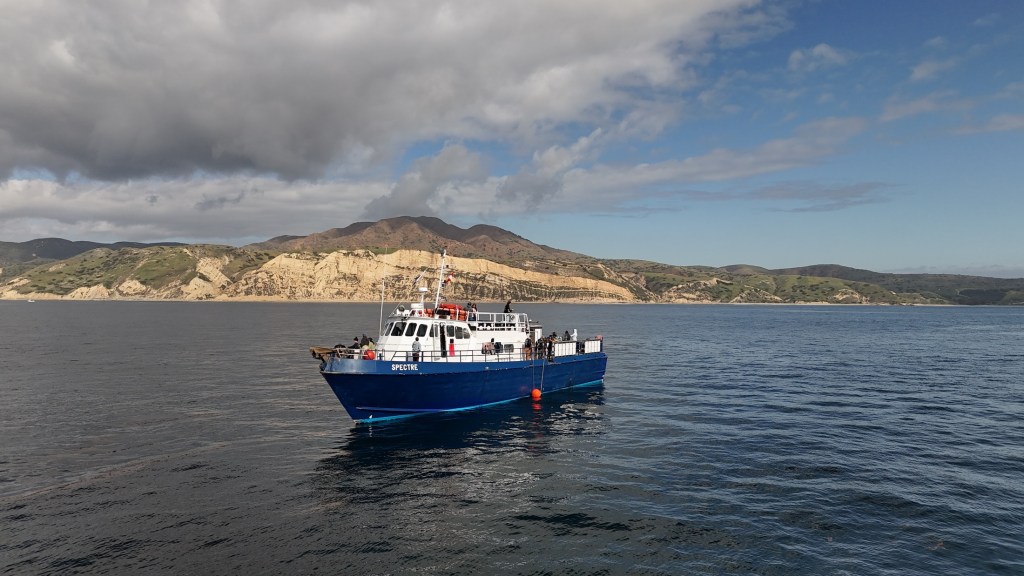
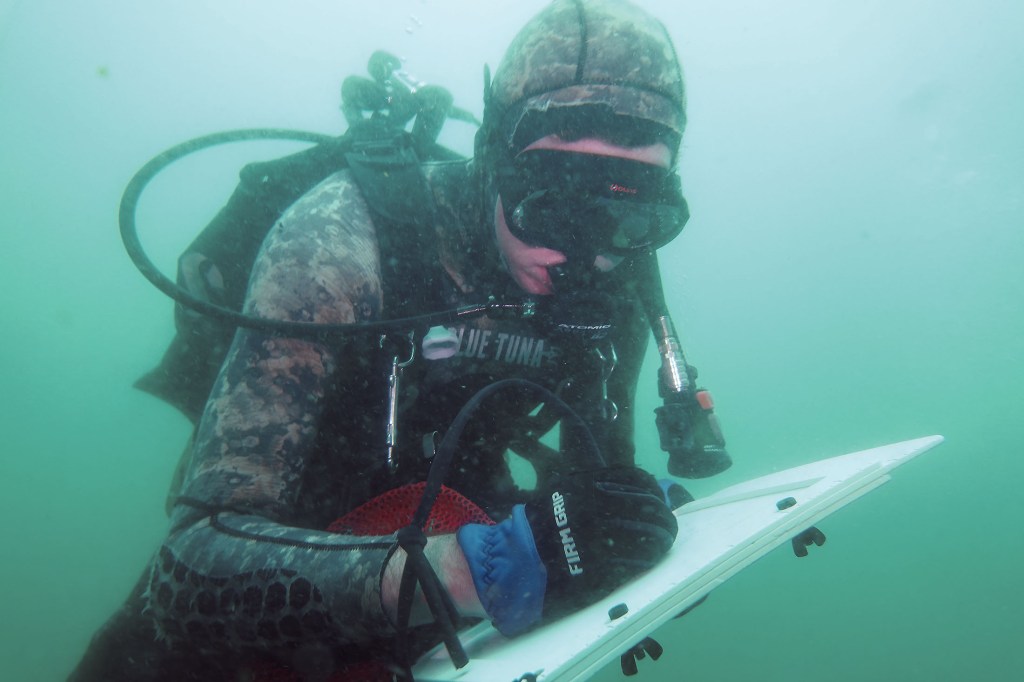
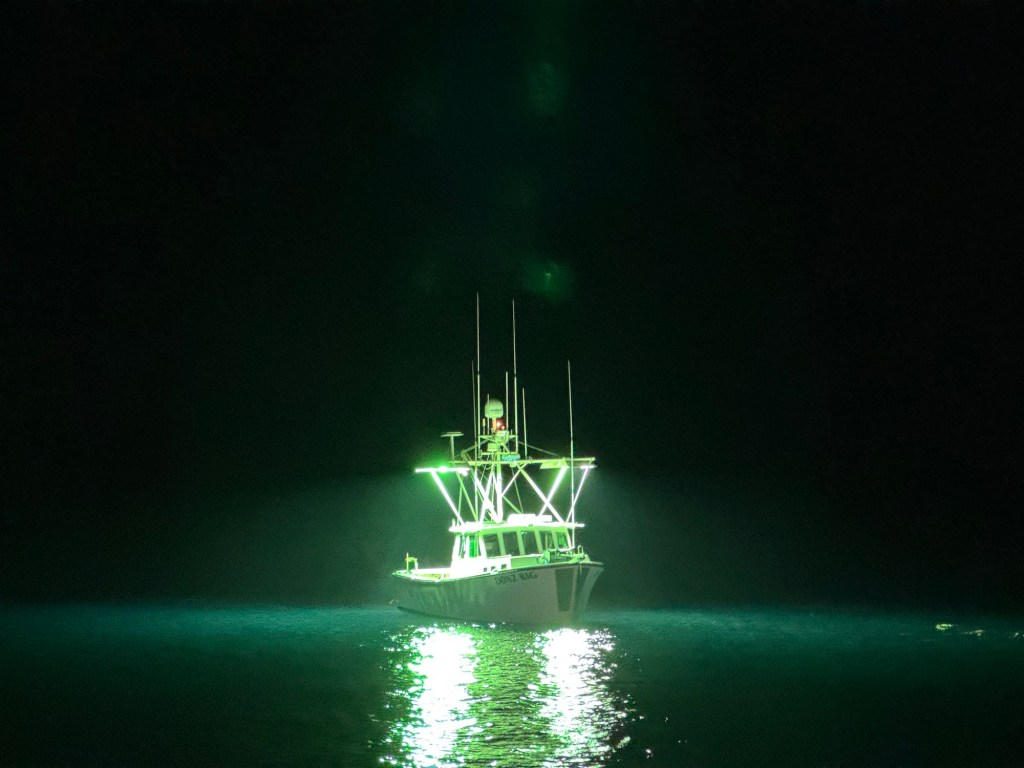
A few months ago, I took a fishing trip out to the western side of San Clemente Island. I woke at two in the morning to the rattle of the anchor chain dropping and stepped out onto the deck, expecting darkness all around us. Instead the night was alive with a strange glow. Dozens of squid boats floated offshore, their powerful lights illuminating the water with a bluish, Avatar-like brightness. The lights draw squid toward the surface before the crews scoop them up in nets.
As I knew from earlier research, and from being a long-time California resident, squid are one of California’s top commercial fisheries, a multimillion-dollar industry built around what is known as market squid. They thrive in enormous numbers in the deep waters around the Channel Islands and up toward Santa Barbara, even though the average beachgoer rarely thinks about them. From the rail of the fishing boat I was I could see vast swarms just below the surface.

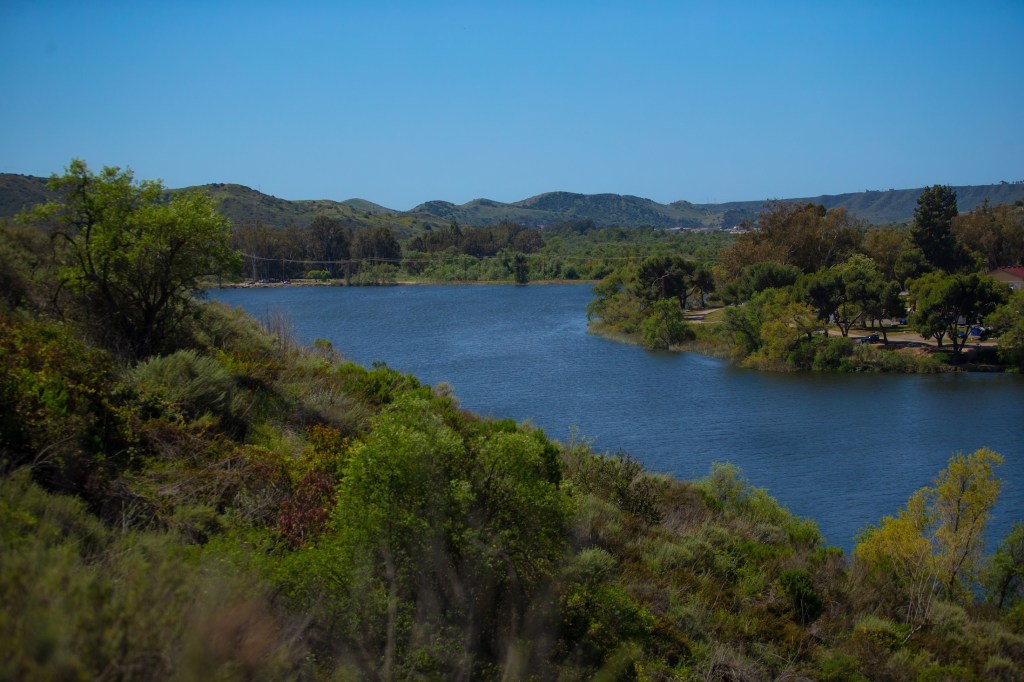
When dawn broke, San Clemente Island emerged ahead of us, and I was struck by how stark and empty it looked. In both directions stretched the same raw, rugged coastline, with almost no sign of human presence (there were what appeared to be radio towers on the top of a peak, but no people).
It felt desolate and otherworldly. But the reality is more complicated.
The island is part of the Channel Islands, a chain that trends east to west rather than the usual north–south pattern of most California ranges. The Channel Islands are often called North America’s Galápagos because they support an extraordinary number of species found nowhere else, shaped by the deep isolation that defines island biogeography (we wrote about this earlier).

San Clemente is no exception. The island is abundant in wildlife, with its own collection of rare plants and animals. But what makes it stand apart from the other islands is the scale of the military activity just beyond the barren cliffs. The U.S. Navy conducts constant training here, including missile tests, amphibious landings, and live-fire exercises. The island is considered one of the most important training grounds for the United States military, operating around the clock even as endangered species cling to survival in the canyons and plateaus nearby.
San Clemente Island looks like a long volcanic ridge from offshore, but it has been one of the most important and least visible military landscapes in California for almost a century. It is the southernmost of the Channel Islands and has been owned entirely by the U.S. Navy since the late 1930s. Over time it became a central part of Naval Base Coronado, and today its main airfield supports helicopters, jets, drones, and special operations teams that rotate through the island throughout the year.
It all seemed really interesting. I desperately wanted to go ashore, but if I’d tried, I almost certainly would have been arrested.
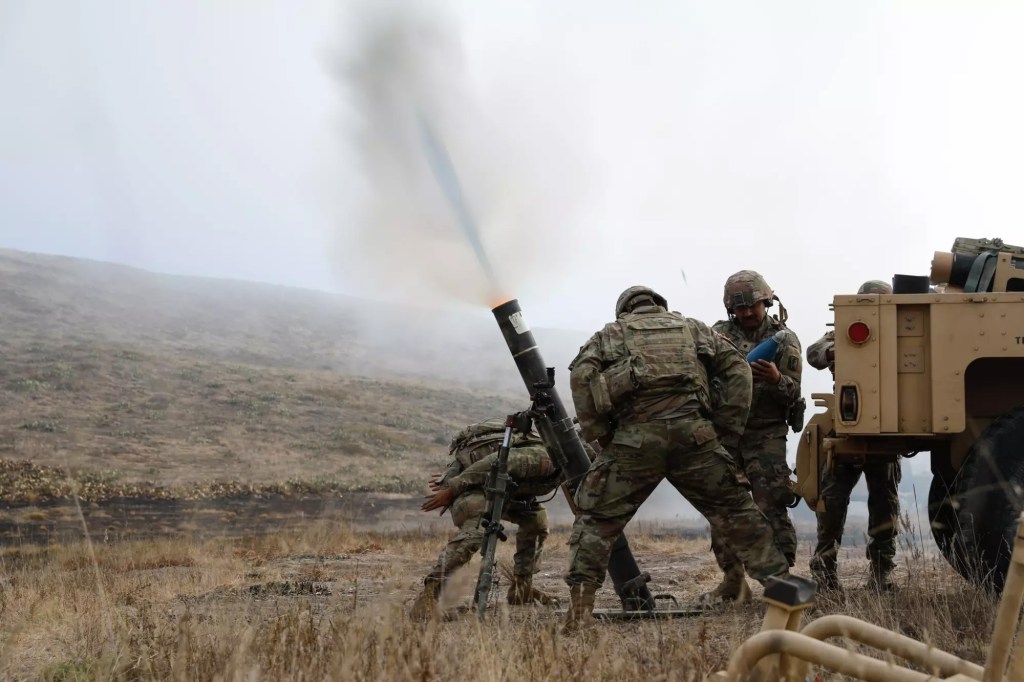

The island began shaping military history just before World War II. In 1939, naval engineers brought early versions of the Higgins boat to San Clemente Island to test how they handled surf, wind, and timing with naval gunfire. These flat-bottomed landing craft became essential to Allied victories in places like Normandy and Guadalcanal. The island’s rugged shoreline helped the US military refine the tactics behind the amphibious assaults that defined twentieth century warfare.
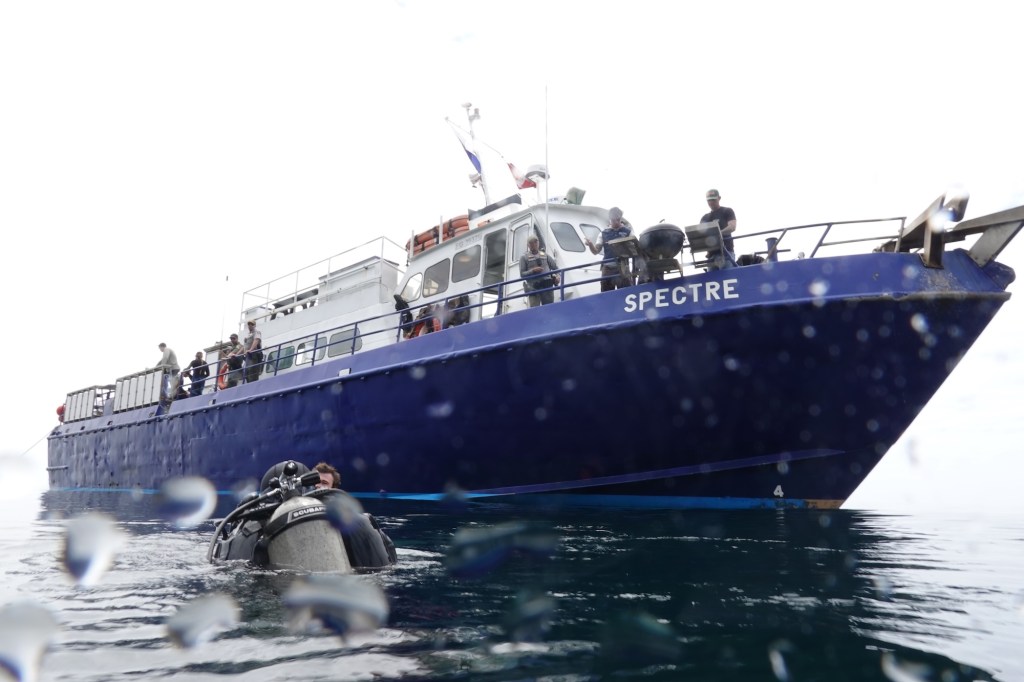
During the Cold War, San Clemente Island evolved into one of the Navy’s busiest live fire training sites. The waters around Pyramid Cove hosted decommissioned ships used as targets. Carrier air wings practiced bombing runs across the southern plateau. Marine units rehearsed ship-to-shore landings on isolated beaches, while submarines conducted simulated missions under restricted airspace. We did a short video you can watch here.
Few places on the West Coast allowed sea, air, and land forces to operate together with real weapons, and the island’s remoteness made it ideal for rehearsing missions that couldn’t take place near populated coastlines. Yet all of this is happening just about 60 miles offshore from Los Angeles. (It took us about five hours to get back).

Civilian access has always been extremely limited, which is why the island only reaches the news when something unusual happens. One widely reported event occurred in 2023, when a private pilot illegally landed a small plane on the island’s runway and then stole a Navy truck before being detained. He tried again in 2025. This kind of thing underscores how isolated and tightly controlled the installation is. For the most part, the only people who ever set foot on the island are service members using it as a sophisticated, real world training environment.
Oh, and scientists, too.
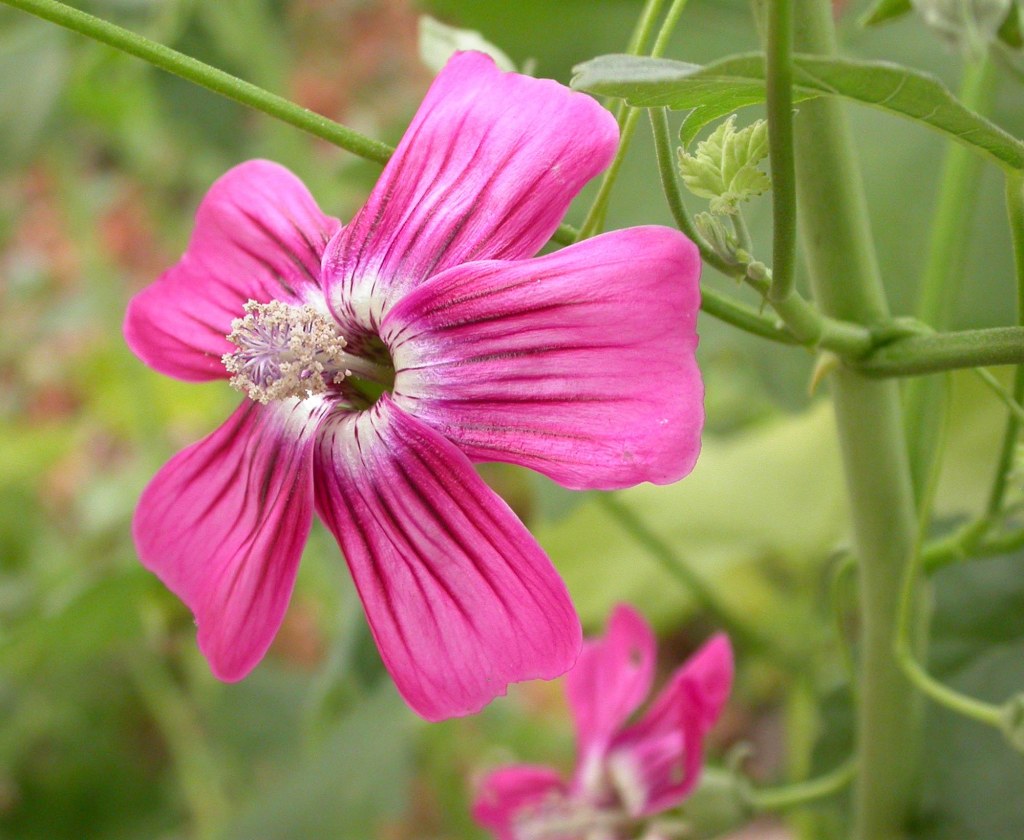
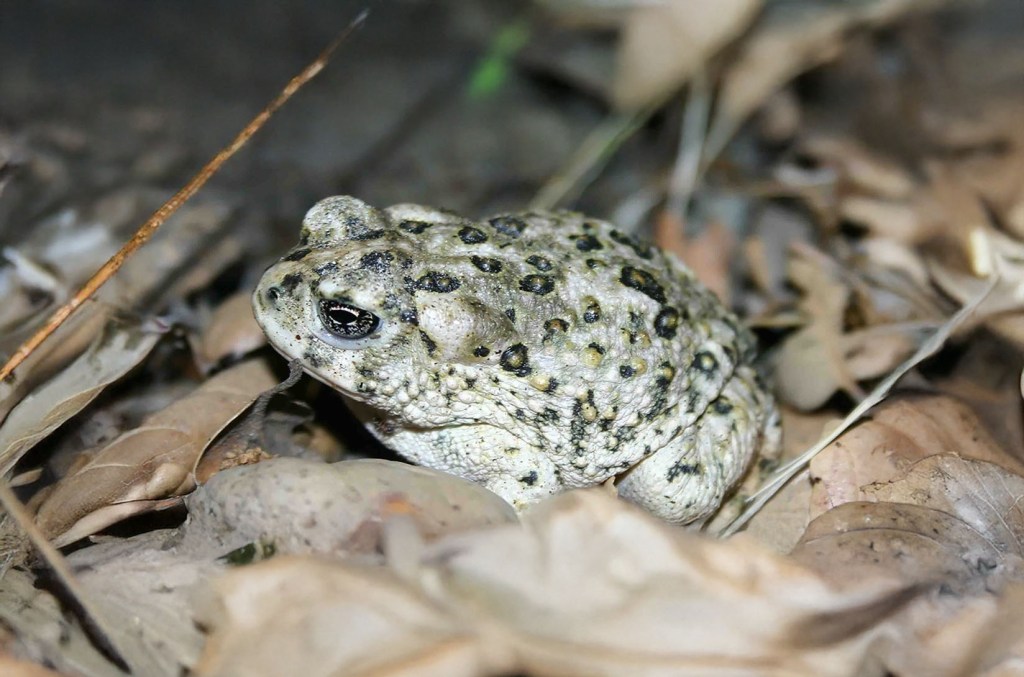
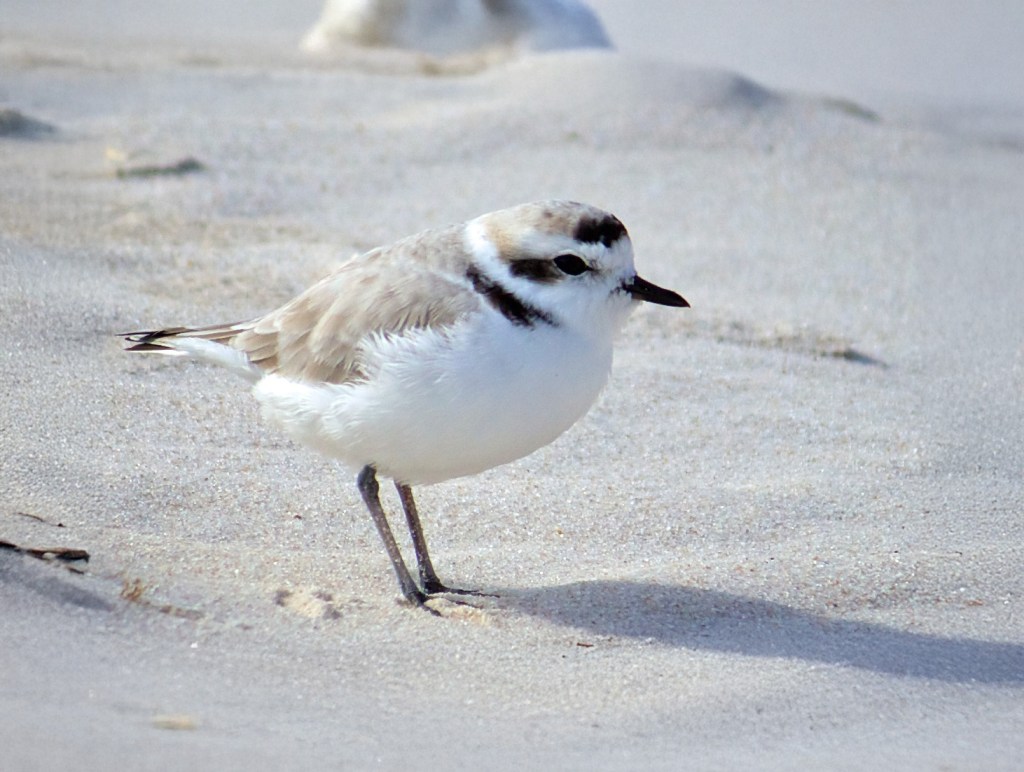
That’s because the island’s natural history has been studied intensively. Decades ago, ranching introduced goats, sheep, and invasive plants that stripped vegetation from entire hillsides. Feral cats and rats preyed greedily on ground nesting birds, and live fire exercises fragmented habitat. By the 1970s and 1980s, San Clemente Island held one of the highest concentrations of endangered species in California, but everything was under threat.

Enter the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, which worked with the military to balance military readiness with the legal requirements of the Endangered Species Act. And it’s been, by many measures, a pretty major success.
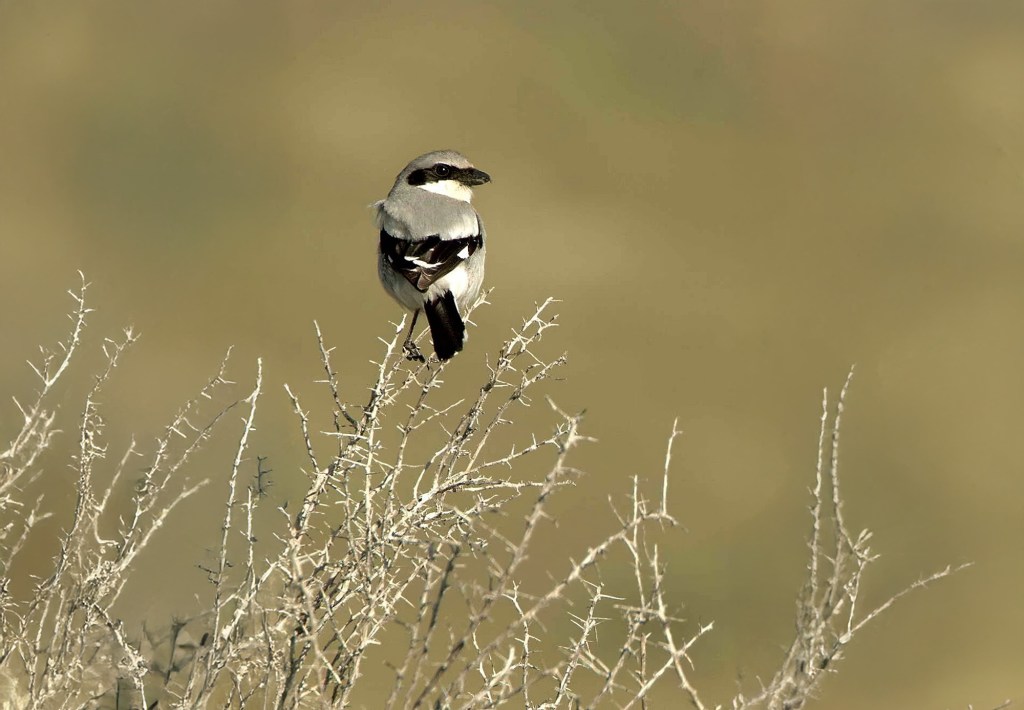
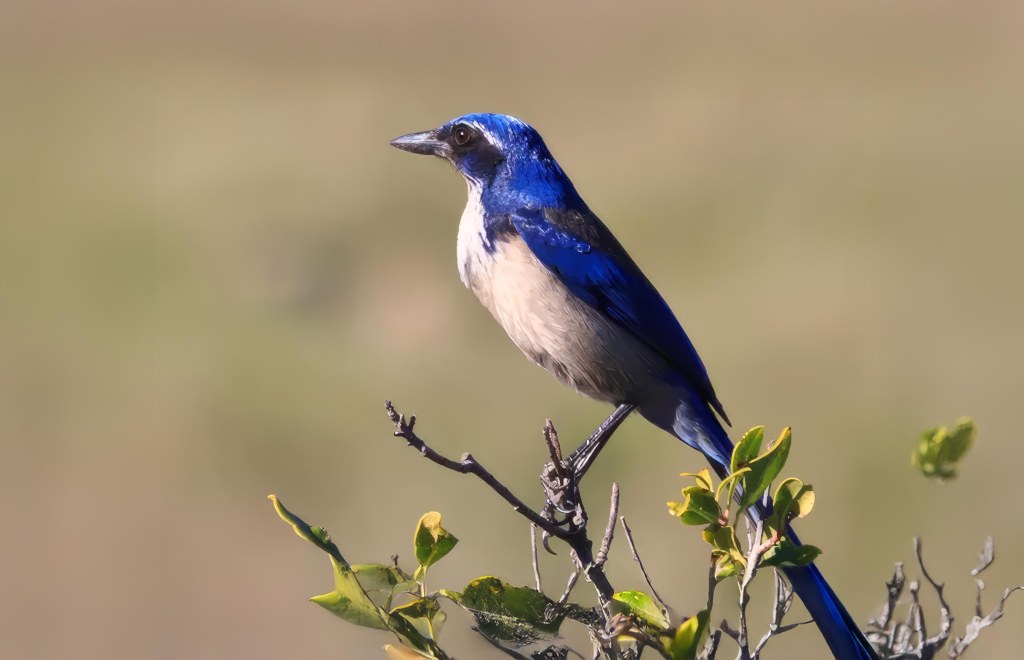
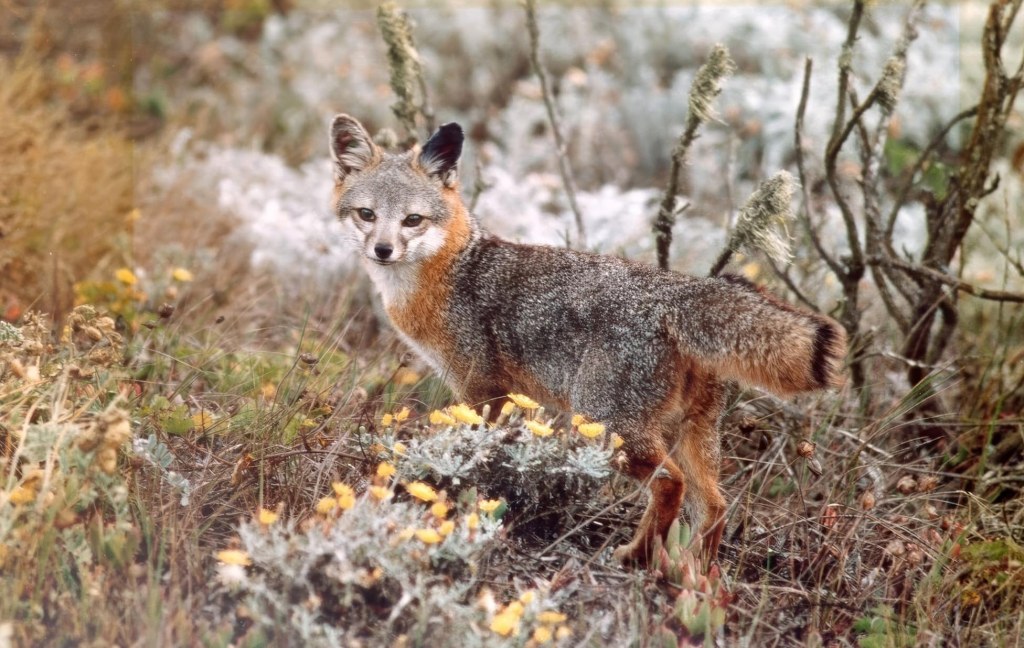
No species became more symbolic of the struggle to protect the island than the San Clemente loggerhead shrike, a lovely, black masked songbird that lives nowhere else on Earth. By the late 1990s its wild population had fallen to as few as fourteen individuals. The Navy funded a comprehensive recovery effort that included captive breeding, predator removal, and habitat reconstruction, all with the expertise help of the San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance. By restoring vegetation and extensive breeding, scientists released shrikes which eventually began to hunt, build territories, and raise their young. The species is now considered one of the most successful island bird recoveries in North America.

And that wasn’t the only success. Once goats and sheep were removed, native shrubs and herbs began returning to the island. Endemic plants such as the San Clemente Island lotus and San Clemente Island paintbrush, responded quickly once the pressure from grazing disappeared. In 2023, after decades of habitat recovery, the Fish and Wildlife Service announced that five island species were healthy enough to be removed from the endangered species list, a pretty cool milestone that suggested a major ecological turnaround for San Clemente and the Channel Islands as a whole.

Today, San Clemente Island remains one of the most unusual places in California. It is a live fire training range where carrier groups, SEAL teams, and Marines rehearse some of the most complex operations in the Navy. It is also a refuge where rare birds and plants have recovered after hovering near extinction. Conservation biologists and military planners now coordinate schedules, field surveys, and habitat protections to keep both missions intact. There’s an excellent documentary on this recovery effort made by SoCal PBS.
California has become a national leader in restoring damaged ecosystems. And while the state has lost much of its original wildness over the centuries, it also offers some of the most compelling examples of species and habitats recovered from the brink. San Clemente Island is more ecologically stable today than at any point in the past century, and it continues to serve as one of the Navy’s most valuable training grounds.