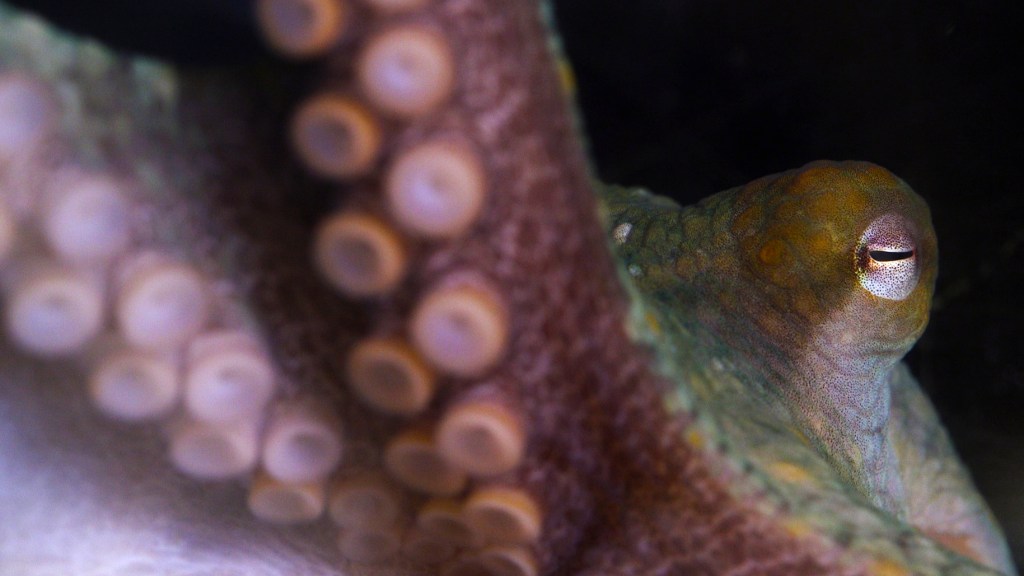
I have a deep passion for octopuses. I have made several short documentaries about them and even traveled twice to Indonesia with one of the world’s leading octopus scientists to film them in their natural habitat. My home office is packed with octopus imagery and iconography, and years ago I made a personal vow never to eat octopus. Squid and other mollusks still get a pass in my book. If you want to debate the ethics of this, fine.
The octopus is a singularly unique creature in the animal kingdom. They are essentially related to clams and abalone and snails, yet they possess an intelligence (let alone a body form) that is so strange and alien, it is unsurprising that sci-fi movies like Arrival feature creatures that are both very intelligent and octopus-like. If you have ever spent an hour alone on the seafloor with an octopus (as I have….just looking eye to eye), you know that they are something different. While most other fish swim away, an octopus will often linger and even engage in what might be considered play.
In fact, we’ve learned that octopuses rely heavily on learning rather than instinct. Unlike many animals that follow hardwired behavioral scripts, octopuses explore, test, and improvise. For that reason and others, it’s hard not to think of them more like other familiar mammals, like a dog or a dolphin.
And then you consider evolution and it gets really weird.

That’s the thing. When we talk about smart animals, we tend to think of vertebrates: dolphins, whales, dogs, horses, elephants. They all share a long evolutionary lineage with us, shaped by natural selection into social, communicative, problem-solving creatures whose minds we recognize because they work in ways familiar to our own. But octopuses are not like that. They diverged from our lineage hundreds of millions of years ago. The last common ancestor humans share with an octopus was a simple wormlike creature. From that fork in the tree of life, vertebrates developed one path toward cognition while invertebrates followed others, some of them evolving remarkable abilities (spiders anyone?!), but rarely what we traditionally call intelligence.
Somehow, the octopus broke that pattern. It built a mind through a completely different architecture, with neurons spread throughout its arms, distributed processing, and behaviors that suggest curiosity, play, memory, strategy. They’ve developed these complex behaviors because they are essentially large blobs of protein moving about the seafloor. When exposed, they are very vulnerable, and so millions of years of evolutionary pressure have compelled them to become, well, smart. What makes this even stranger is how short their lives are…usually just a year or two. All of that intelligence compressed into what, in the grand scheme of things, is just a brief flash of existence.

Alongside them, their closest cousins, the cuttlefish, have evolved similarly striking cognitive abilities, but they don’t quite equate with the octopus. Still, together they show that intelligence is not a single climb up one evolutionary ladder but something nature can shape in entirely different ways. Convergent evolution.
So, if you were searching for meaning and purpose and trying to understand the process of intelligence itself, you could hardly find a better creature to study than the octopus. Short of discovering another intelligent life form somewhere in the universe, the octopus is one of our best bets to grasp what intelligence is and how it evolves.

Scientists are doing precisely that right now. And there is one species they turn to the most: our own California two-spot octopus (Octopus bimaculoides), one of the most remarkable animals on the planet. (They get their name, obviously, from the attractive blue spots on their sides.) The California two-spot octopus spends its days tucked into small crevices and hunting right off our shores. You can see them up and down the coast. I have only encountered a few in the wild, but each time it’s special, like a Christmas gift.

What’s especially cool is that the California two-spot octopus has gone from a coastal curiosity — an animal long seen, admired, and loved by divers — to a full-fledged scientific model, teaching us new things about neuroscience, genomics, and behavior. In 2015, researchers published the first complete genome sequence of the California two-spot octopus, and it marked a watershed moment in the study of cognition. For the first time, scientists could look directly at the genetic architecture behind an intelligence built on an evolutionary branch completely separate from our own. The two-spot became the go-to organism for this work because it is abundant in local waters, manageable in laboratory settings, and displays a level of problem solving that can be tested and observed in controlled conditions. I guess they make great pets, too, because several folks on Instagram have them and make pretty entertaining videos with them.
The genome of the two-spot octopus turned out to carry a treasure trove of evolutionary surprises. One of the most striking discoveries was the massive expansion of protocadherin genes, which guide how neurons connect and communicate. Vertebrates like humans have them, too, but octopuses have many more. This genetic abundance appears tailored to their unusual nervous system. Roughly two-thirds of an octopus’s neurons are not in its central brain but distributed throughout its arms. Each arm can process sensory information and make decisions locally, while still coordinating with the rest of the animal.
According to Roger Hanlon, who I have worked with, octopuses are colorblind, and yet they have this remarkable ability to change color to fit their surroundings. It may be the most remarkable camouflage ability in the animal world, and yet we still understand surprisingly little about how it works. In addition to neurons, their skin and arms appear to contain opsins, light-detecting cells, raising the possibility that octopuses do not just see with their eyes, but with their bodies as well.
I mean, does it get more alien than that? That’s the stuff of serious sci-fi.

The genome also revealed a wide set of genes involved in learning, neural flexibility, and sensory perception. Many of the same kinds of genes that support cognition in vertebrates appear in octopuses too, but they have been expanded and reworked, suggesting that evolution arrived at intelligence using a very different blueprint.
Perhaps the most surprising discovery is the octopus’s heavy reliance on RNA editing. RNA editing is the process by which cells deliberately alter RNA after it has been copied from DNA. If DNA is the master blueprint, RNA is the working set of instructions, and in octopuses that working copy can be extensively rewritten, especially in the nervous system. While other animals can do this on a small scale, this unusual molecular flexibility in the octopus may help their nervous systems adapt and respond with a level of speed and sophistication that maybe helps explain their problem-solving abilities and behavioral creativity, even if scientists are still working out exactly how it all works.
We’re really at the beginning of an effort to better understand this animal’s remarkable abilities and how it compares with our own unique intelligence. What we have learned so far is that octopus intelligence is real, measurable, and deeply unusual. In experiments, octopuses can solve puzzles, open jars, navigate mazes, remember solutions over time, and learn by watching others. Stories of octopuses escaping their tanks, squirting water at people they recognize, or slipping away from handlers they seem to dislike are surprisingly common. When I was a summer docent at the National Museum in Washington D.C. many years ago, there was an octopus that would greet me by draping an arm over the edge of the glass whenever I came in. Walking up to the tank felt less like approaching an exhibit and more like being welcomed by a friend.
Yes, I know, there is real danger in anthropomorphizing animals.

Many of my friends who are aware of my love for these animals beseeched me to watch My Octopus Teacher, the Oscar-winning documentary film. I’ve seen it twice, and I have to say that while I love many of the shots and scenes in the film, I feel like the movie goes way overboard making these animals seem like they have human emotions. I’m not sure they do. Something else is going on, I’m just not sure what it is.
If you’d like a good book on the subject, I’d recommend Other Minds: The Octopus, the Sea, and the Deep Origins of Consciousness by Peter Godfrey-Smith. It’s got more actual science in it than Sy Montgomery’s The Soul of an Octopus: A Surprising Exploration into the Wonder of Consciousness, which, like My Octopus Teacher, kind of annoyed me.
All of this is to say that we are blessed here in California to have such an amazing species in our local waters. The California two-spot octopus is more than an interesting coastal species; it is a window into how minds can form in ways we never imagined. Its genome offers clues to the very nature of intelligence, demonstrating that cognition can arise from wholly different evolutionary routes. In that sense, studying this unassuming little animal on our shoreline may be the closest we come to understanding an alien mind without ever leaving Earth.