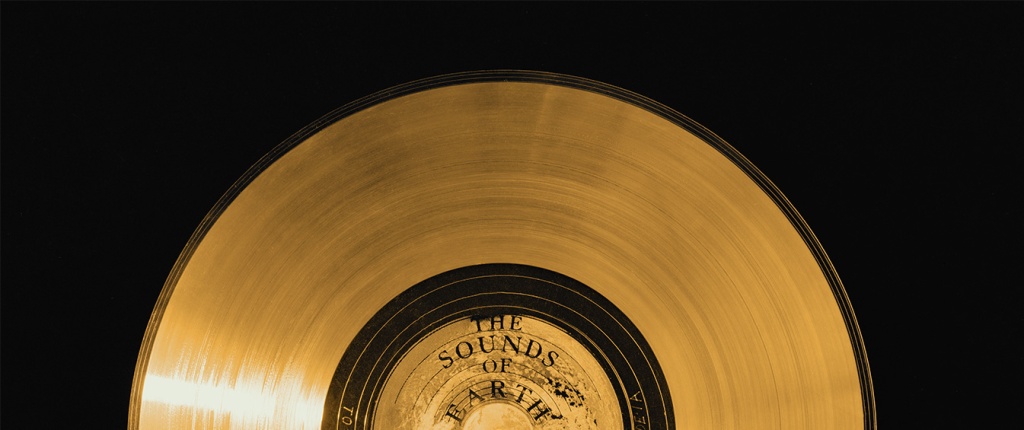
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in La Canada Flintridge, California is well-known for building and sending spacecraft far into the cosmos to help us better understand the universe. But the agency was also extensively involved in one of the most ambitious and symbolic projects in the history of space exploration, one that in many ways was more art than science: the Voyager Golden Record.
In 1977, as the twin Voyager spacecraft prepared to journey beyond the confines of our solar system, they carried with them what might be the most profound artifacts ever created by humanity: the Voyager Golden Records. These records, designed to last a billion years, are time capsules intended not for Earthlings but for potential extraterrestrial finders or future humans. Engraved in gold-plated copper discs, the records encapsulate the Earth’s diverse cultural and natural heritage—from music to languages to sounds of nature.

The idea of the Golden Record was developed by a talented team led by Carl Sagan, the renowned astronomer and science communicator. Sagan, alongside other prominent figures such as Frank Drake, Ann Druyan, science journalist Jon Lomberg, and Linda Salzman Sagan, crafted a selection that aimed to represent the entirety of Earth. The content ranged from classical music by Bach and Beethoven to greetings in 55 languages, natural sounds like thunderstorms and whales, and a diverse set of 115 images depicting life and culture on Earth.
But producing a record that could survive the harsh environment of space, while also being understandable and playable by beings of unknown technology, posed unique challenges. This is where the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) stepped in, playing a pivotal role in transforming this ambitious vision into a tangible, durable artifact capable of traversing the cosmos.

Photo: NASA/JPL-Cal Tech
JPL, managed by Caltech under a NASA contract, was primarily responsible for the construction and operation of the Voyager spacecraft. Their expertise was crucial not just in the scientific instrumentation and engineering of the spacecraft but also in integrating the Golden Records. The lab’s engineers worked meticulously to ensure that the records were equipped with everything needed for potential playback: a cartridge, a needle, and symbolic instructions detailing their use. These instructions, etched onto the record’s cover, provided a universal map indicating Earth’s location in relation to pulsar stars, which are highly stable and can be used as galactic landmarks.
JPL’s involvement extended to the actual physical preparation of the records. They coordinated closely with RCA Records to produce the master disc from which the Voyager records were replicated. The final products were then plated in gold and encased in a protective aluminum jacket, designed to withstand the vacuum of space, cosmic rays, and extreme temperatures.

The technical contributions of JPL ensured that the Golden Records were not only a feat of cultural expression but also a marvel of scientific and engineering ingenuity. By equipping the Voyager spacecraft with these messages, JPL helped bridge the human desire to explore and communicate with the tangible reality of space travel. The records, mounted aboard Voyagers 1 and 2, continue to be ambassadors of Earth, carrying sounds, music, and images intended to convey the story of our world to whoever, or whatever, might find them.

Today, both Voyager spacecraft, with their Golden Records, have entered interstellar space, marking them as the most distant human-made objects in existence. They serve as reminders of humanity’s ambition to reach beyond our immediate grasp and to communicate across vast cosmic distances. JPL’s role in this historic endeavor highlights the profound connection between human creativity and technological advancement, ensuring that our message to the cosmos will endure long after the original voices have faded.

Photo: NASA/JPL-Cal Tech
As these records voyage through the cosmos, they remind us not just of where we have been, but also of the far reaches that our curiosity can take us. Through the combined efforts of visionaries like Carl Sagan and the engineering prowess of JPL, the Voyager Golden Record stands as a testament to the best of human knowledge, culture, and technological achievement.
The Voyager Golden Records are phonograph records, much like the vinyl records used to listen to music before digital media became widespread. They are constructed from copper discs coated in gold to withstand the harsh environment of space. Each record is encased in a protective aluminum jacket, along with a cartridge and a needle. Instructions in symbolic language explain the origin of the spacecraft and indicate how the record should be played. The playback speed (16 2/3 revolutions per minute) is much slower than typical records, which typically spin at 33 1/3 or 45 rpm.
The content of the Golden Record is a meticulously curated selection intended to represent the diversity of life and culture on Earth:
Sounds of Earth: The records include audio of nature sounds like thunder, wind, and animals (including the songs of birds and whales). Human sounds like footsteps, a heartbeat, and laughter are also embedded, capturing the biological and social essence of Earth.

Musical Selections: There are 27 musical tracks from different cultures and eras, ranging from classical pieces by Bach and Beethoven to traditional songs from various cultures, including a Navajo chant and a Peruvian wedding song. These selections were intended to showcase the diversity of musical expression on Earth.
Greetings in 55 Languages: A variety of spoken greetings from “Hello” in English to ancient languages like Akkadian. The inclusion of a broad range of languages aims to depict the linguistic diversity of humanity.
Images: The record also contains 115 analog-encoded photographs and diagrams. These images show a wide range of subjects, including humans of different sexes and races, everyday activities, scientific knowledge like mathematical definitions, and the Solar System. The intent was to offer a visual summary of our planet and its inhabitants.

CALIFORNIA CURATED ART ON ETSY
Purchase stunning art prints of iconic California scenes.
Check out our Etsy store.
Message from the UN Secretary-General and the President of the United States: There are also printed messages from prominent global leaders at the time, including U.S. President Jimmy Carter and United Nations Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim.
Sounds of Human Origin: Beyond natural and environmental sounds, the record also includes a montage of the sounds of Earth, a screaming chimpanzee, a medley of human-originated noises like tools, vehicles, and a kiss, among others.
The idea behind the Voyager Golden Record is not just to communicate where and who we are but also to share a message of hope and peace with any possible recipient, even if that recipient is far in the future. The chances of the Voyager spacecraft actually being found by extraterrestrial life are slim, but the Golden Record serves as a profound gesture of goodwill and a testament to the human spirit’s longing to reach out and explore the universe.