“Man is a geologic agent,” the late California geologist Eldridge Moores.
Roadcuts in California, those slices through hills and mountainsides made during the construction of roads, are like open books to geologists. They reveal the intricate and often dramatic geological history of the state. When you drive along the highways of California, you’re likely to pass by these exposed cliffs of rock. To the everyday traveler, they might just be a part of the landscape, but to geologists, they are invaluable windows into the Earth’s past.
““Geologists on the whole are inconsistent drivers. When a roadcut presents itself, they tend to lurch and weave,” wrote the great geology (and many other topics) writer John McPhee in his excellent book Annals of the Former World. “To them, the roadcut is a portal, a fragment of a regional story, a proscenium arch that leads their imaginations into the earth and through the surrounding terrane.”

Roadcuts expose layers of rock that have been hidden from view for millions of years. Each layer, or stratum, tells a story of what the environment was like when that layer was deposited. By studying these layers, geologists can reconstruct a timeline of events that shaped the region. For example, they can identify periods of volcanic activity, times when the area was submerged under an ancient ocean, or epochs when massive glaciers were carving out the valleys.

California is especially interesting due to its active tectonic setting. It’s not just the San Andreas Fault that captivates geologists; there are numerous lesser-known faults that crisscross the state, and roadcuts can expose these hidden fractures. By studying the composition of rocks along these faults, geologists learn about the nature of past seismic activity and can make predictions about future earthquakes.
The rock composition in California varies widely, offering a rich tapestry of geological history. In the Sierra Nevada, granite roadcuts tell of a time when massive chambers of magma slowly cooled and crystallized deep beneath the Earth’s surface. Elsewhere, roadcuts through sedimentary rocks like sandstone and shale may contain fossils, giving clues about the life forms that once inhabited the region.

These man-made artifacts also reveal the forces that have shaped California’s diverse landscapes. In roadcuts, geologists might find evidence of powerful geological processes such as metamorphism, where existing rock types are transformed into new types due to high pressure and temperature conditions. For instance, the presence of metamorphic rocks like schist and gneiss can indicate ancient collision zones where Earth’s tectonic plates have crashed together.
The value of California roadcuts is wonderfully illustrated in John McPhee’s “Assembling California.” The book is an excellent narrative that weaves the tale of California’s complex geology with the lives of the geologists who study it. Eldridge Moores, a late prominent geologist from the University of California, Davis (Moores died in 2018), played a significant role in deciphering the geological history of the region, particularly through his fieldwork involving roadcuts.

At the time Eldridge Moores entered the field, the theory of plate tectonics was only beginning to gain traction. In the early 1960s, the idea that continents drifted and that vast slabs of the Earth’s crust moved over the mantle was still controversial, met with skepticism by many geologists trained in older, fixist models. Moores, however, embraced the theory early, recognizing in it an explanation for the chaotic structures he saw in California’s mountain belts. As a young researcher, he studied the Troodos ophiolite in Cyprus, an exposed section of ancient oceanic crust, and realized that similar rock assemblages—serpentinized peridotites, deep-sea sediments, and basaltic lavas—were scattered across California.
“It was a very exciting time. I still get goosebumps even talking about it,” Moores told KQED in 2017. “A turning point, I think it was, in the plate tectonic revolution, that was the watershed of geology.”
With plate tectonics as a guiding framework, Moores understood that these rocks were remnants of vanished oceans, relics of seafloor that had been uplifted and accreted onto the edge of North America. His work helped reveal that much of California had arrived in pieces, a geological patchwork of island arcs, deep-sea basins, and continental fragments welded together by subduction. While others were still debating the validity of plate tectonics, Moores was already applying it, using it to decode the assembly of an entire state.

Moores was renowned for his work on ophiolites, sections of the ocean floor that have been thrust up onto the continent. One of his notable discoveries was the identification of ophiolite sequences in the roadcuts along the highways of the Sierra Nevada. These discoveries were crucial in understanding the ancient tectonic movements that shaped western North America.
Through roadcuts, Moores and his colleagues were able to observe and study the juxtaposition of different rock types, providing further evidence for the theory of plate tectonics. They could literally walk along the cuts and see how different terranes—large packets of rock with a distinct geological history—were stitched together like a geological quilt, offering insight into the past locations of tectonic plates.

Purchase stunning coffee mugs and art prints of iconic California species.
Check out our Etsy store.
“Nature is messy,” Moores once told McPhee. “Don’t expect it to be uniform and consistent.”
There are thousands of roadcuts across California, each exposing a fragment of the state’s chaotic geology. The Palmdale Roadcut, a striking geological feature along the San Andreas Fault, has been an invaluable resource for geologists studying the dynamics of this infamous fault line. This natural cut exposes a cross-section of the earth, revealing layers of rock and sediment that have been shifted and shaped by seismic activity over millions of years. The rock here is a chaotic mélange—fault gouge, shattered granite, and twisted layers of sedimentary rock that have been pulverized and ground together by the relentless motion of the Pacific and North American plates. By analyzing these layers, geologists can better understand the history and behavior of the San Andreas Fault, including the patterns of past earthquakes and the movements of tectonic plates. This, in turn, contributes significantly to the broader understanding of seismic risks and aids in preparing for future seismic events.

(Photo: Erik Olsen)
Another geologist, Garniss Curtis, used California roadcuts to study volcanic rocks and their embedded minerals, which allowed for the dating of geologic events with greater precision. His work on the potassium-argon dating method turned roadcuts into time machines, where the age of rocks could be determined with the help of exposed minerals.
One of California’s most well-known roadcuts, the Charlie Brown Outcrop (map), is a favorite among geologists. Located along Highway 178 near the Nevada border, it has been highlighted by geology teacher Garry Hayes, author of the acclaimed Geotripper blog. Hayes says of the roadcut (also known as the Shoshone Roadcut):
“There are really three stories told in this exposure, that of distant ash eruptions, a violent eruption close by, and earthquakes with associated mountain-building.”
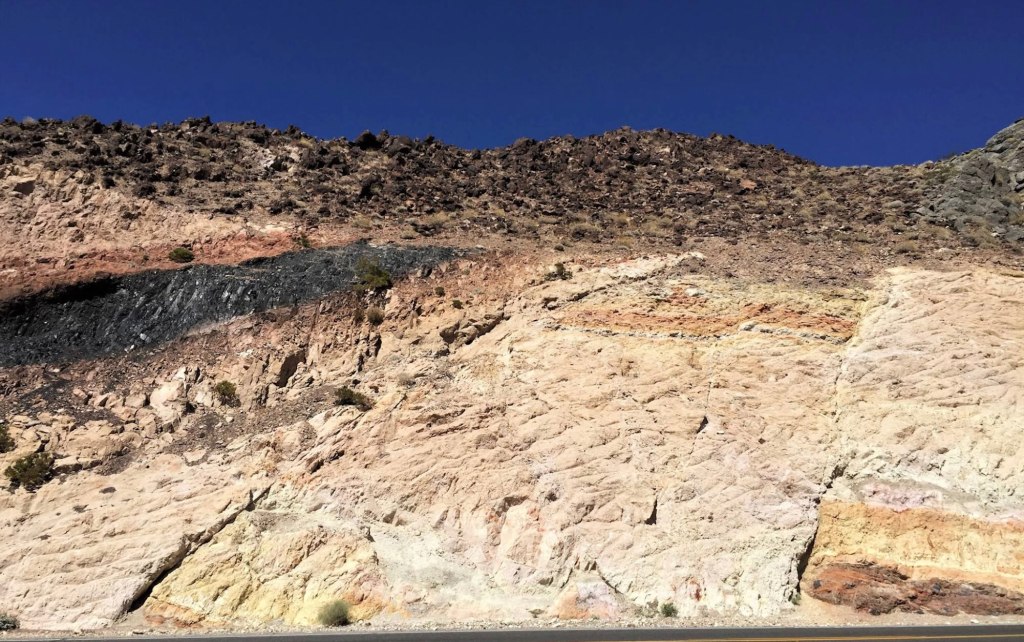

These geologists, among others, have used roadcuts as a means to peel back the layers of time, revealing the processes that have operated to create the state’s diverse geologic scenery. Roadcuts have provided the evidence for groundbreaking theories and have been instrumental in mapping the geological evolution of California. The work of these scientists exemplifies the roadcut’s role as a natural laboratory, a place where Earth’s geologic history is on full display for those who know how to read the rocks.
Moreover, roadcuts are crucial for educating the next generation of geologists. They serve as natural laboratories where students can practice identifying rock types, deciphering the sequence of geological events, and understanding the dynamic forces that continue to shape the Earth.

In Assembling California, McPhee remarked that “geologists are like dermatologists: they study, for the most part, the outermost two per cent of the earth. They crawl around like fleas on the world’s tough hide, exploring every wrinkle and crease, and try to figure out what makes the animal move.”
Manmade creations like roadcuts greatly assist geologists in their work. In essence, roadcuts are not just incidental byproducts of infrastructure development; they are key to understanding California’s complex geological evolution. They tell stories of ancient environments, tectonic upheavals, and the slow but inexorable forces that continue to mold the landscape. For geologists in California, the roadcut is a portal into the deep past, offering a tangible connection to the processes that have made the state what it is today.