A California Company Called MP Materials Hopes to Revitalize Domestic Rare Earth Production to Reduce Dependence on China

Rare earth metals are now essential to the global economy, powering everything from smartphones and electric vehicles to wind turbines and defense systems. As China continues to dominate the market—producing more than 70% of the world’s supply—the urgency to find reliable alternatives has grown. The United States is locked in a high-stakes race to secure new sources of rare earth elements, along with other critical minerals like lithium and nickel, which are key to the clean energy transition. At the center of this effort is a storied mine in California that not only helped launch the rare earth industry decades ago but now stands as America’s most promising hope for rebuilding a domestic supply chain.
Mining shaped California’s growth, from the 1849 Gold Rush to key industries like mercury, silver, copper, tungsten, and boron. While some have declined, others, like the Rio Tinto U.S. Borax Mine in Boron, California, remain major global suppliers, while rare earth element extraction continues to be an important industry.

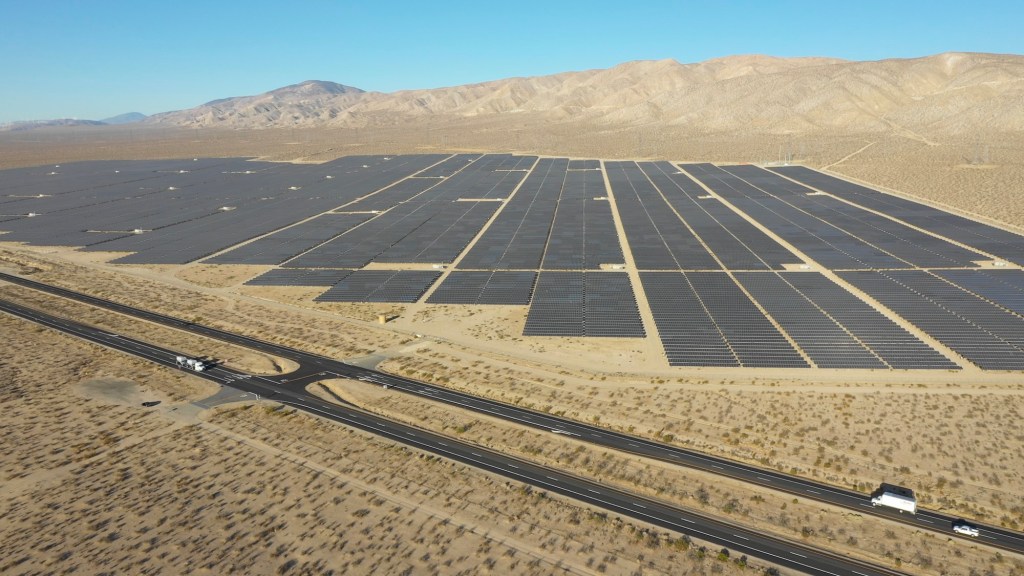
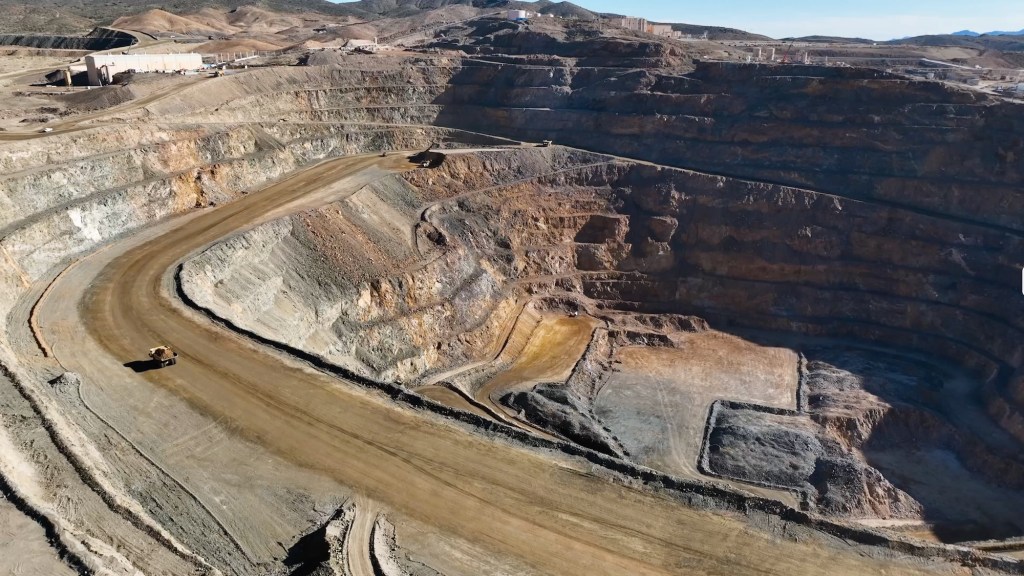
MP Materials’ Mountain Pass rare earths mine in California is a remarkable example of industrial resurgence and the strategic importance of critical metals in the modern era. Located in Mountain Pass in the remote Californian desert near the Nevada border (it’s easily viewable from Interstate 15), this mine, initially developed in the mid-20th century, has seen dramatic shifts in fortune, technology, and geopolitics, reflecting the complex role rare earth elements (REEs) play in global industries.
The rock at Mountain Pass contains an average of 7 to 8 percent rare earth elements—a remarkably high concentration by industry standards. This richness is a key factor in the mine’s potential. However, extracting these valuable elements from the surrounding material remains a challenge.
Discovered in 1949 while prospectors searched for uranium, the Mountain Pass deposit instead revealed bastnaesite, an ore rich in rare earth elements like neodymium, europium, and dysprosium. These elements are indispensable to modern technologies, powering innovations across consumer electronics, environmental solutions, and advanced military systems.

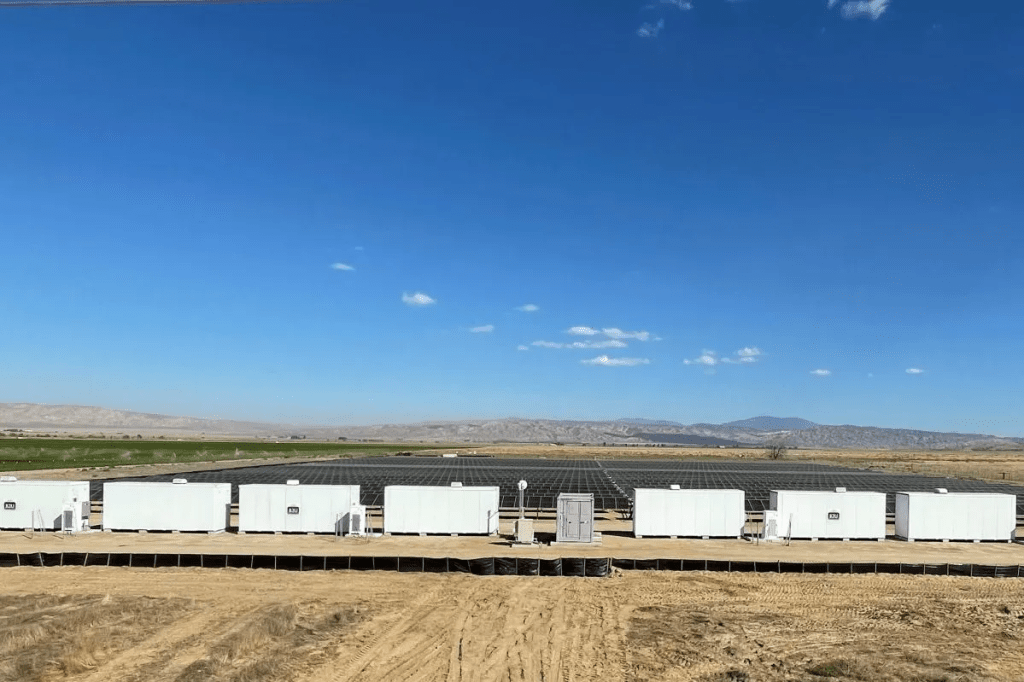
site in Mountain Pass, CA. (Courtesy: MP Materials)
Smartphones, for instance, are packed with rare earth elements that enable their functionality. Europium and gadolinium enhance the brightness and color of their screens. Lanthanum and praseodymium contribute to the efficiency of their circuits, while terbium and dysprosium enable the compact, high-performance speakers. Beyond smartphones, rare earth elements are essential to electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies, particularly in the production of permanent magnets. Thanks to their distinctive atomic structure, rare earth elements can produce magnetic fields far stronger than those generated by other magnetizable materials like iron. This exceptional capability arises from their partially filled 4f electron shell, which is shielded by outer electrons. This configuration not only gives them unique magnetic properties but also results in complex electronic arrangements and a tendency for unpaired electrons with similar spins. These characteristics make rare earth elements indispensable for creating the most advanced and powerful commercial magnets, as well as for applications in cutting-edge electronics.
Permanent magnets are among the most significant uses of rare earths, as they convert motion into electricity and vice versa. In the 1980s, scientists discovered that adding small amounts of rare earth metals like neodymium and dysprosium to iron and boron created incredibly powerful magnets. These magnets are ubiquitous in modern technology: tiny ones make your phone vibrate, medium-sized ones power the wheels of electric cars, and massive ones in wind turbines transform the motion of air into electricity. A single wind turbine can require up to 500 pounds of rare earth metals, highlighting their critical role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.

Additionally, rare earths play a significant role in environmental applications. Cerium is used in catalytic converters to reduce vehicle emissions, while lanthanum enhances the efficiency of water purification systems. Rare earth-based phosphors are employed in energy-efficient lighting, such as LED bulbs, which are central to reducing global energy consumption.
The importance of these elements underpins the strategic value of deposits like Mountain Pass, making the extraction and refinement of rare earths a critical aspect of both technological progress and national security. In the military domain, rare earths are integral to cutting-edge systems. They are used in the production of advanced lasers, radar systems, night vision equipment, missile guidance systems, and jet engines. According the the Department of Defense, for example, the F-35 Lightning II aircraft requires more than 900 pounds of rare earth elements. Alloys containing rare earth elements also strengthen armored vehicles, while lanthanum aids in camera lenses and night vision optics, giving military forces a strategic advantage.

(Courtesy of MP Materials)
To fully appreciate the significance of rare earth elements and their crucial role in the United State’s economic future, it’s essential to explore the history of Mountain Pass, one of the most important rare earth mines in the world. This storied site not only played a pivotal role in meeting the surging demand for these elements but also serves as a case study in the challenges of balancing industrial ambition with environmental responsibility.
The Molybdenum Corporation of America, later renamed Molycorp, initially capitalized on the booming demand for europium in color televisions during the 1960s. In 1952, the company acquired the Mountain Pass site, recognizing its rich deposits of rare earth minerals. As the first major player in rare earths in the United States, it began operations at Mountain Pass, establishing a foothold in the burgeoning industry. Over the ensuing decades, Mountain Pass became the world’s premier source of rare earths, serving a growing market for advanced materials.
By the 1990s, however, the mine faced significant challenges. Environmental damage caused by leaks of heavy metals and radioactive wastewater led to regulatory scrutiny and costly fines, culminating in the mine’s closure. During its dormancy, global rare earth production shifted overwhelmingly to China, which gained near-monopoly control over the market. By the time Molycorp attempted to revive the site in the early 2000s, it struggled against operational inefficiencies, low rare earth prices, and fierce Chinese competition. Molycorp eventually declared bankruptcy, leaving the mine idle once again.
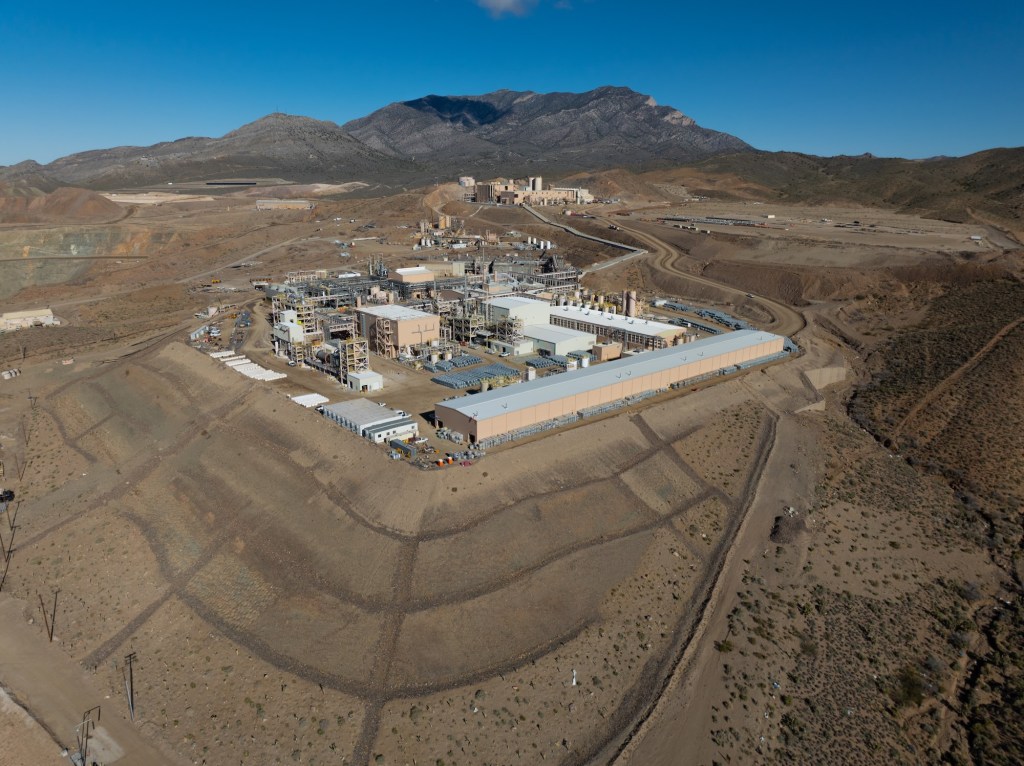

In 2017, MP Materials, led by investors including Michael Rosenthal and Jim Litinsky, acquired the shuttered Mountain Pass mine after recognizing its untapped potential. Initially, they anticipated an established mining or strategic buyer would emerge. Faced with the risk of losing the mine’s permit and seeing it permanently closed through reclamation, they made the bold decision to operate it themselves. To restart operations, MP Materials partnered with Shenghe Resources, a Chinese state-backed company that provided critical early funding and became the company’s primary customer. Through this arrangement, MP shipped raw rare earth concentrate to China for processing, laying the foundation for a business model that was heavily reliant on the Chinese supply chain.
Over the next several years, Mountain Pass far exceeded expectations. By 2022, it was producing 42,000 metric tons of rare earth oxides—three times the best output achieved under its previous owner, Molycorp—and accounted for about 15% of global production. In 2024, the mine hit a U.S. production record with over 45,000 metric tons of REO in concentrate. But even as the mine’s output surged, MP Materials’ ties to China remained central to its operations. Shenghe not only purchased the bulk of that concentrate but also maintained an 8% ownership stake. In 2024, roughly 80% of MP’s revenue came from this relationship. That changed in 2025, when China imposed steep tariffs and new export restrictions. MP responded by halting all shipments to China, shifting instead to processing much of its output domestically and selling to U.S.-aligned markets like Japan and South Korea. It has since invested nearly $1 billion to build out a full domestic supply chain and launched a joint venture with Saudi Arabia’s Ma’aden, marking a decisive pivot away from reliance on China.
The processing of rare earth elements, particularly for high-value applications like magnets, involves a complex, multi-step value chain. It begins with extraction, where ores containing rare earths are mined, followed by beneficiation, a process that concentrates the ore to increase its rare earth content. Next, separation and refining isolate individual rare earth oxides through solvent extraction or other chemical methods. These refined oxides then undergo metallization, where they are reduced into their metallic form, making them suitable for further industrial use. The metals are then alloyed with other elements to enhance their properties, and finally, the material is shaped into high-performance magnets essential for applications in electric vehicles, wind turbines, and advanced electronics. Each of these steps presents significant technical, economic, and environmental challenges, making rare earth processing one of the most intricate and strategically important supply chains in modern technology.
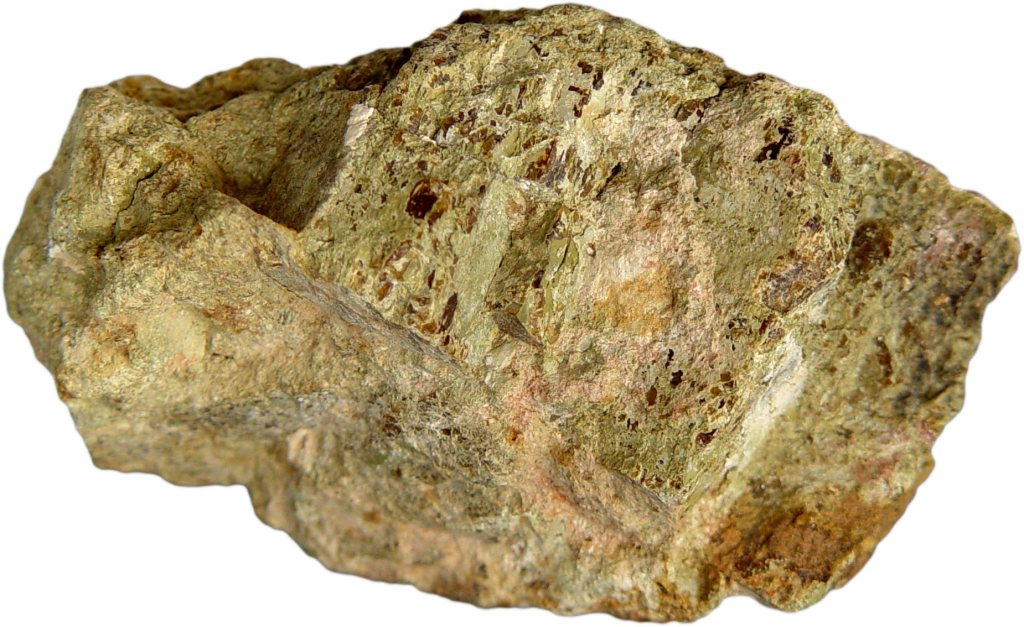

Despite MP Materials’ success and efforts to ramp up facets of processing at its Mountain Pass mine in California, a critical portion of the rare earth refining process—metallization, alloying, and magnet manufacturing—remains dependent on other countries, including China and Japan. These procedures are both intricate and environmentally taxing, and California’s stringent regulatory framework, designed to prioritize environmental protections, has made domestic processing particularly challenging. Across the rare earths industry, this dependence on Chinese facilities exposes a significant vulnerability in the rare earth supply chain, leaving the United States and other countries reliant on foreign infrastructure to produce critical materials essential for technologies such as electric vehicles and advanced military systems.
However, to address the dependency on foreign processing, MP Materials is investing heavily in building a fully domestic rare earth supply chain. At its Mountain Pass mine in California, the company is enhancing its processing and separation capabilities to refine rare earth elements on-site. Meanwhile, at its new Independence facility in Fort Worth, Texas, MP Materials has begun producing neodymium-praseodymium (NdPr) metal and trialing sintered neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets. This facility marks the first domestic production of these critical materials in decades, with the capability to produce 1,000 metric tons of magnets annually, amounting to the production of roughly half a million EV motors.
“This is our ultimate goal,” says Matt Sloustcher, EVP of Corporate Affairs for MP Materials. “To handle the entire separation and refining process on-site—but that ramp-up takes time.”
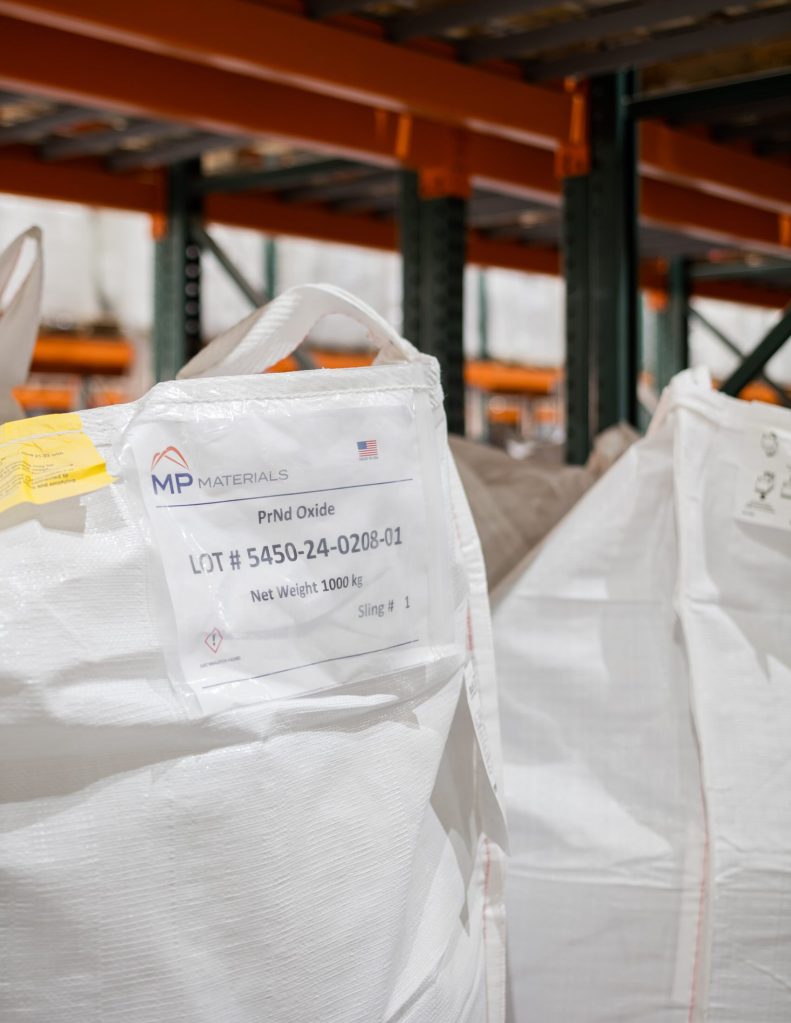

MP Materials asserts that the new U.S.-based rare earth supply chain it is developing will be a “zero discharge” facility, recycling all water used on-site and disposing of dry waste in lined landfills. That will make it a far more environmentally sustainable than its counterparts in Asia, where rare earth mining and processing have led to severe pollution and ecological damage. The company says it is making progress. MP Materials’ Sloustcher pointed California Curated to a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) study published in the American Chemical Society which “found that NdFeB magnets produced from Mountain Pass ore have about one-third the environmental footprint of those from Bayan Obo, China’s largest rare earth mine.”
“With record-setting upstream and midstream production at Mountain Pass and both metal and magnet production underway at Independence , we have reached a significant turning point for MP and U.S. competitiveness in a vital sector,” said James Litinsky, Founder, Chairman, and CEO of MP Materials in a company release.
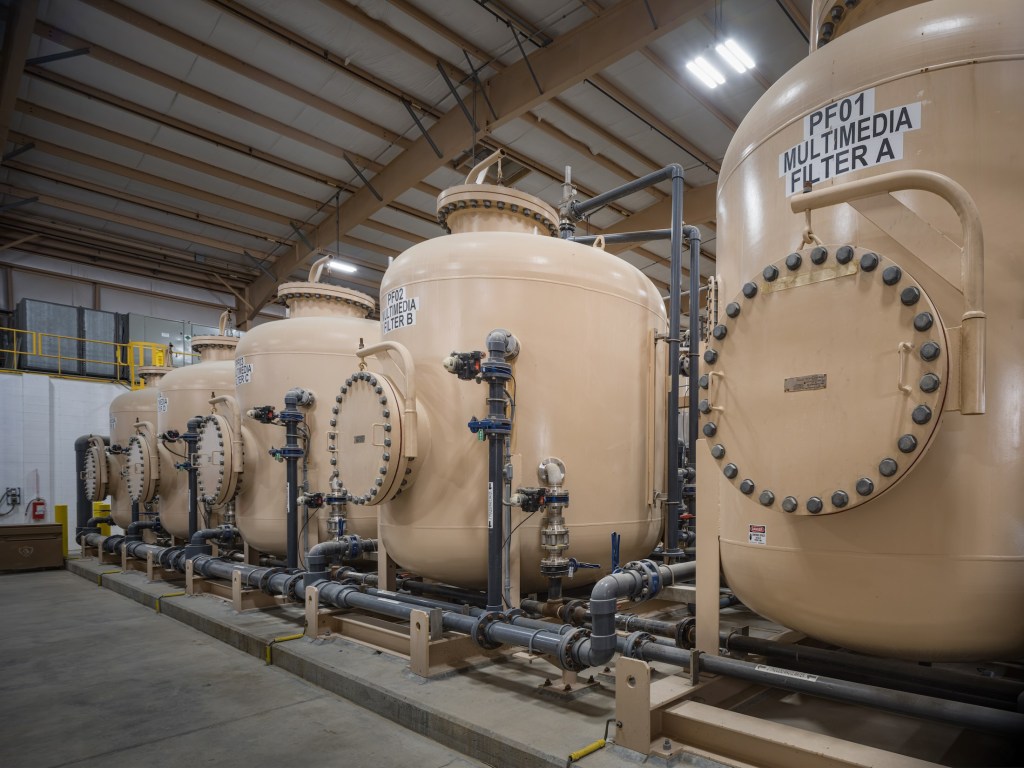

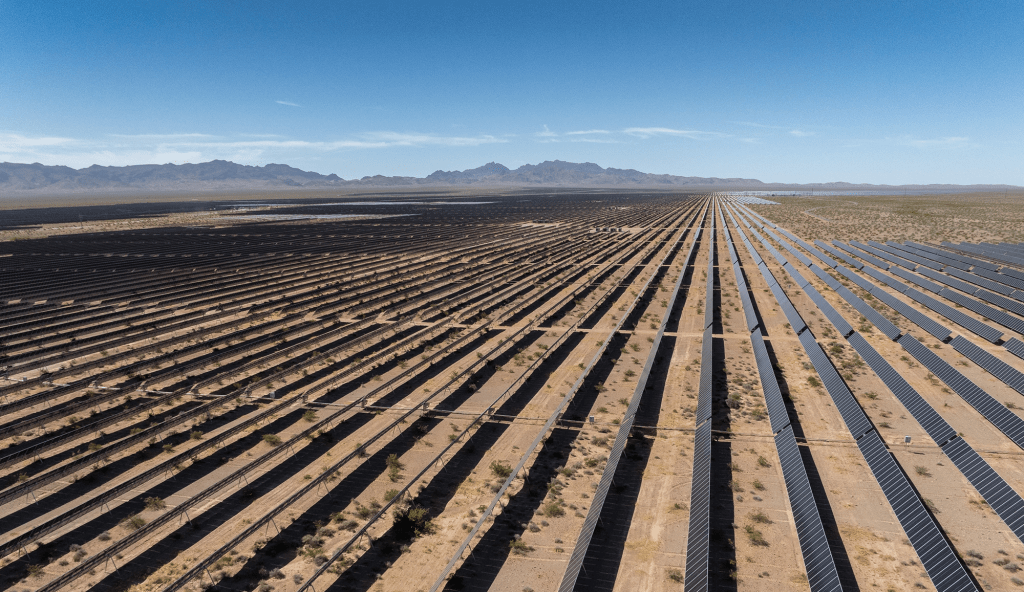
Mountain Pass, CA. (Courtesy: MP Materials)
MP Materials has also partnered with General Motors to produce rare earth magnets for electric vehicles, signaling its commitment to integrating domestic production into key industries. The push for domestic EV production is not just about economic security but also about environmental sustainability, as reducing the carbon footprint of mining, processing, and transportation aligns with the broader goal of clean energy independence.
The resurgence of the Mountain Pass mine aligns with a broader initiative by the U.S. government to secure domestic supplies of critical minerals. Recognizing Mountain Pass as a strategic asset, the Department of Defense awarded MP Materials a $35 million contract in February 2022 to design and build a facility for processing heavy rare earth elements at the mine’s California site Additionally, the Department of Energy has been actively supporting projects to strengthen the domestic supply chain for critical minerals, including rare earth elements, through various funding initiatives.

Visit the California Curated store on Etsy for original prints showing the beauty and natural wonder of California.
Mountain Pass’s operations, however, highlight the challenges inherent in mining rare earths. The extraction process involves significant environmental risks, particularly in managing wastewater and tailings ponds. MP Materials claims to prioritize sustainable practices, yet its long-term ability to minimize environmental impact while scaling production remains under scrutiny. The mine’s bastnaesite ore, with rare earth concentrations of 7–8%, is among the richest globally, making it economically competitive. Still, as mentioned above, processing bastnaesite to isolate pure rare earth elements involves complex chemical treatments, underscoring why global production remains concentrated in a few countries.
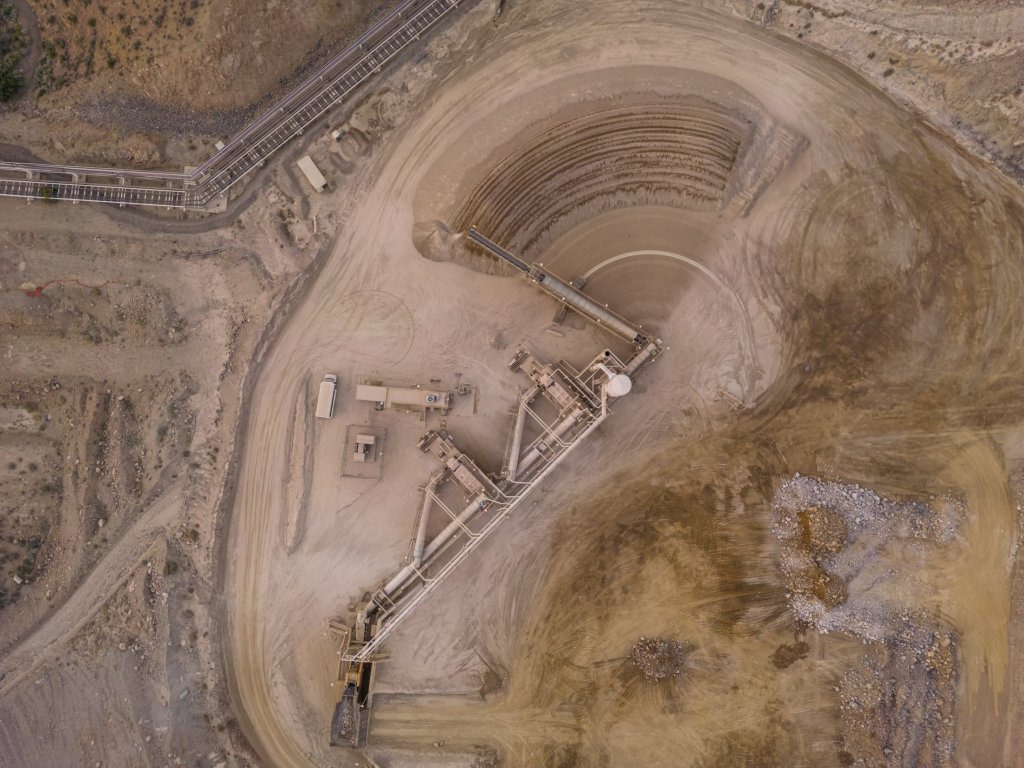

Today, Mountain Pass is not only a critical supplier but also a symbol of U.S. efforts to reduce dependency on Chinese rare earth exports as well as other minerals such as lithium and copper vital to a transition to clean energy technology. As demand for REEs surges with advancements in green energy and technology, the increasing mine’s output supports the production of permanent magnets used in electric motors, wind turbines, and countless other applications. This resurgence in domestic rare earth production offers hope for a revitalized U.S.-based supply chain, reducing dependence on foreign sources and ensuring a more stable, sustainable future for critical mineral access.
However, significant obstacles remain, including the environmental challenges of mining, the high costs of refining and processing, and the need to develop advanced manufacturing infrastructure. Overcoming these barriers will require coordinated efforts from industry, government, and researchers to make domestic production both economically viable and environmentally responsible, ensuring a truly climate-friendly future. With the global race for critical minerals intensifying, MP Materials’ success demonstrates the potential—and challenges—of revitalizing domestic mining infrastructure in an era of heightened resource competition.