In California’s southeastern desert, the Salton Sea stretches across a wide, shimmering basin, a lake where there shouldn’t be one. At about 340 square miles, it’s the state’s largest lake. But it wasn’t created by natural forces. It was the result of a major engineering failure. I’ve long been fascinated with the place: its contradictions, its strangeness, its collision of nature and human ambition. It reflects so many of California’s tensions: water and drought, industry and wilderness, beauty and decay. And it was only relatively recently that I came to understand not just how the Salton Sea came to exist, but how remarkable the region’s geological past really is, and how it could play a major role in the country’s sustainable energy future.
In the early 1900s, the Imperial Valley was seen as promising farmland: its deep, silty soil ideal for agriculture, but the land was arid and desperately needed irrigation. To bring water from the Colorado River, engineers created the Imperial Canal, a massive infrastructure project meant to transform the desert into productive farmland. But the job was rushed. The canal had to pass through the Mexican border and loop back into California, and much of it ran through highly erodible soil. Maintenance was difficult, and by 1904, silt and sediment had clogged portions of the canal.
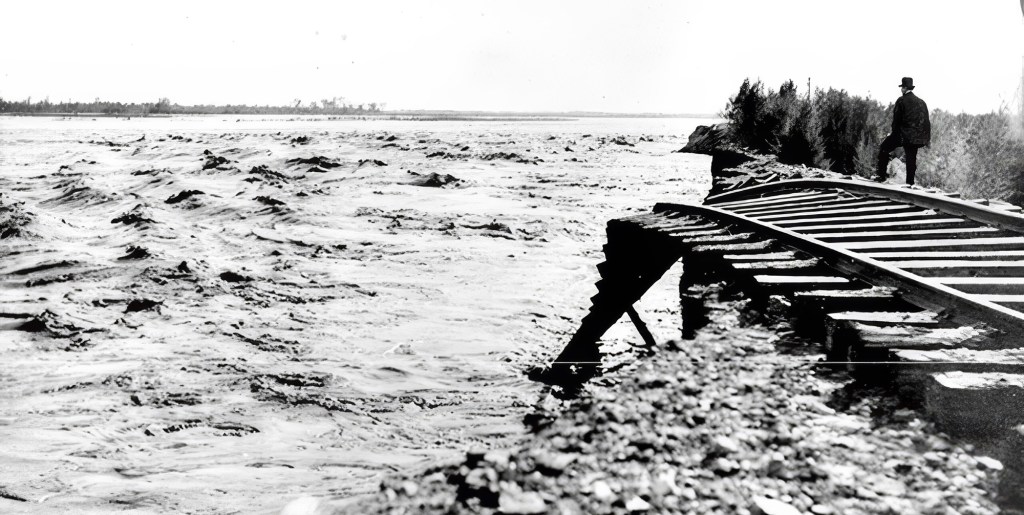

To keep water flowing, engineers hastily dug a temporary bypass channel south of the clogged area, hoping it would only be used for a few months. But they failed to build proper headgates, critical structures for controlling water flow. In 1905, an unusually heavy season of rain and snowmelt in the Rockies caused the Colorado River to swell. The torrent surged downriver and overwhelmed the temporary channel, carving it wider and deeper. Before long, the river completely abandoned its natural course and began flowing unchecked into the Salton Sink, an ancient, dry lakebed that had once held water during wetter epochs but had long since evaporated. (This has happened many times over in the region’s history).
For nearly two years, the Colorado River flowed uncontrolled into this depression, creating what is now known as the Salton Sea. Efforts to redirect the river back to its original course involved a frantic, expensive engineering campaign that included the Southern Pacific Railroad and U.S. government assistance. The breach wasn’t fully sealed until early 1907. By then, the sea had already formed: a shimmering, accidental lake nearly 35 miles long and 15 miles wide, with no natural outlet, in the middle of the California desert.
In the 1950s and early ’60s, the Salton Sea was a glamorous desert escape, drawing crowds with boating, fishing, and waterskiing. Resorts popped up along the shore, and celebrities like Frank Sinatra, Jerry Lewis, Rock Hudson, the Beach Boys, and the Marx Brothers came to visit and perform. It was billed as a new Palm Springs with water, until rising salinity and environmental decline ended the dream. There have been few if any similarly starge ecological accidents like it.

The creation of the Salton Sea was both a blessing and a curse for the people of the Imperial Valley. On the one hand, the lake provided a new source of water for irrigation, and the fertile soil around its shores proved ideal for growing crops. On the other hand, the water was highly saline, and the lake became increasingly polluted over time, posing a threat to both human health and the environment.
Recently, with most flows diverted from the Salton Sea for irrigation, it has begun to dry up and is now considered a major health hazard, as toxic dust is whipped up by heavy winds in the area. The disappearance of the Salton sea has also been killing off fish species that attract migratory birds.

The New York Times recently wrote about the struggles that farmers face as the Salton Sea disappears, and how the sea itself will likely disappear entirely at some point.
“There’s going to be collateral damage everywhere,” Frank Ruiz, a program director with California Audubon, told the Times. “Less water coming to the farmers, less water coming into the Salton Sea. That’s just the pure math.”

To me, the story of the Salton Sea is fascinating: a vivid example of how human intervention can radically reshape the environment. Of course, there are countless cases of humans altering the natural world, but this one feels particularly surreal: an enormous inland lake created entirely by accident, simply because a river, the Colorado, one of the most powerful in North America, was diverted from its course. It’s incredible, and incredibly strange. What makes the region even more fascinating, though, is that the human-made lake sits in a landscape already full of geological drama.
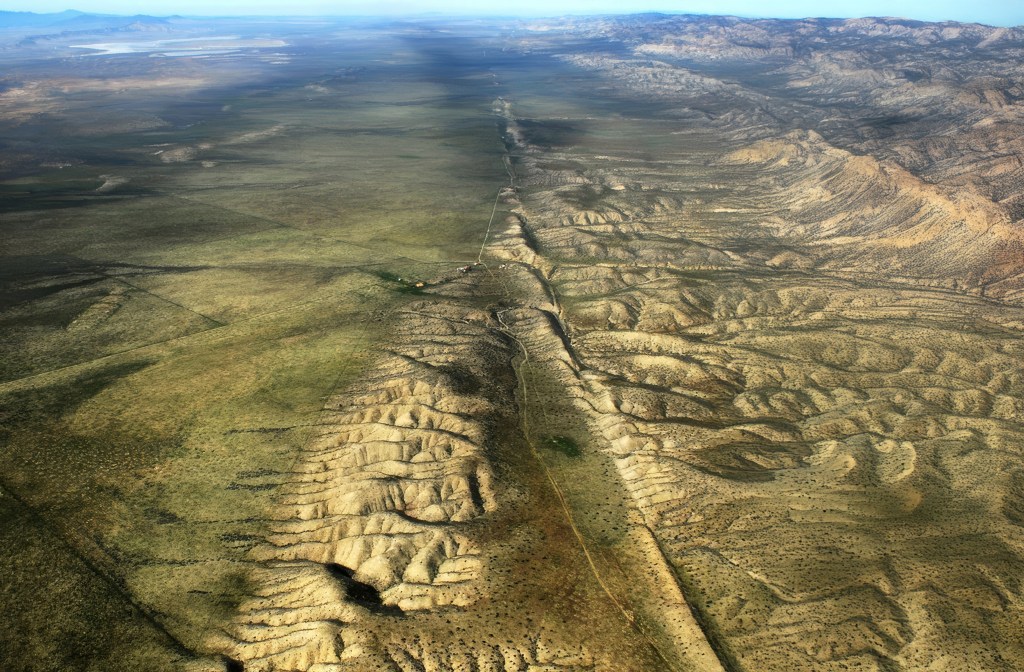
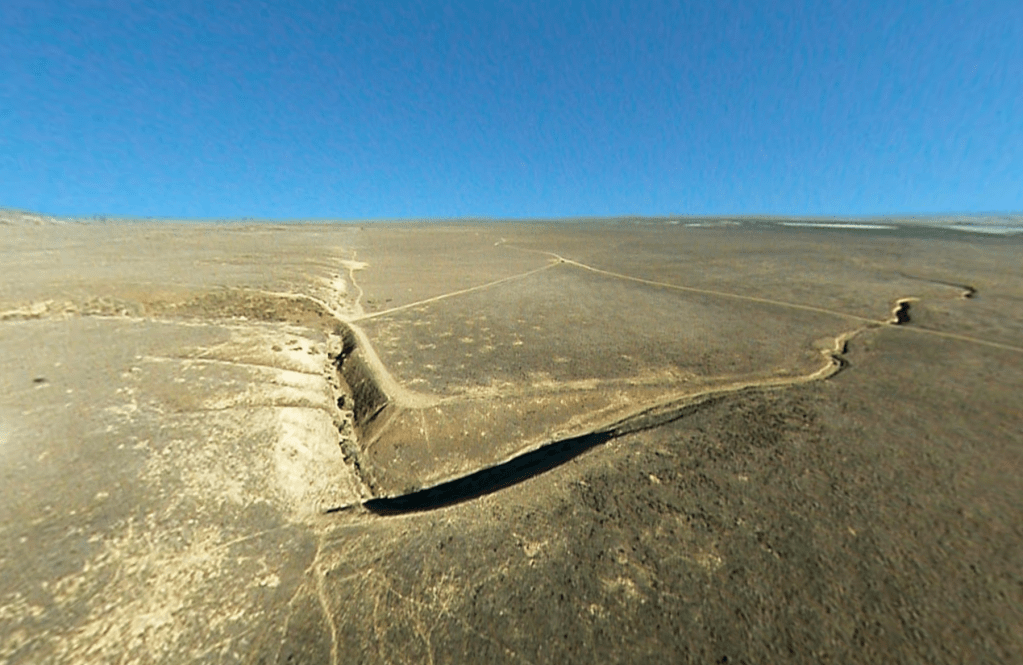
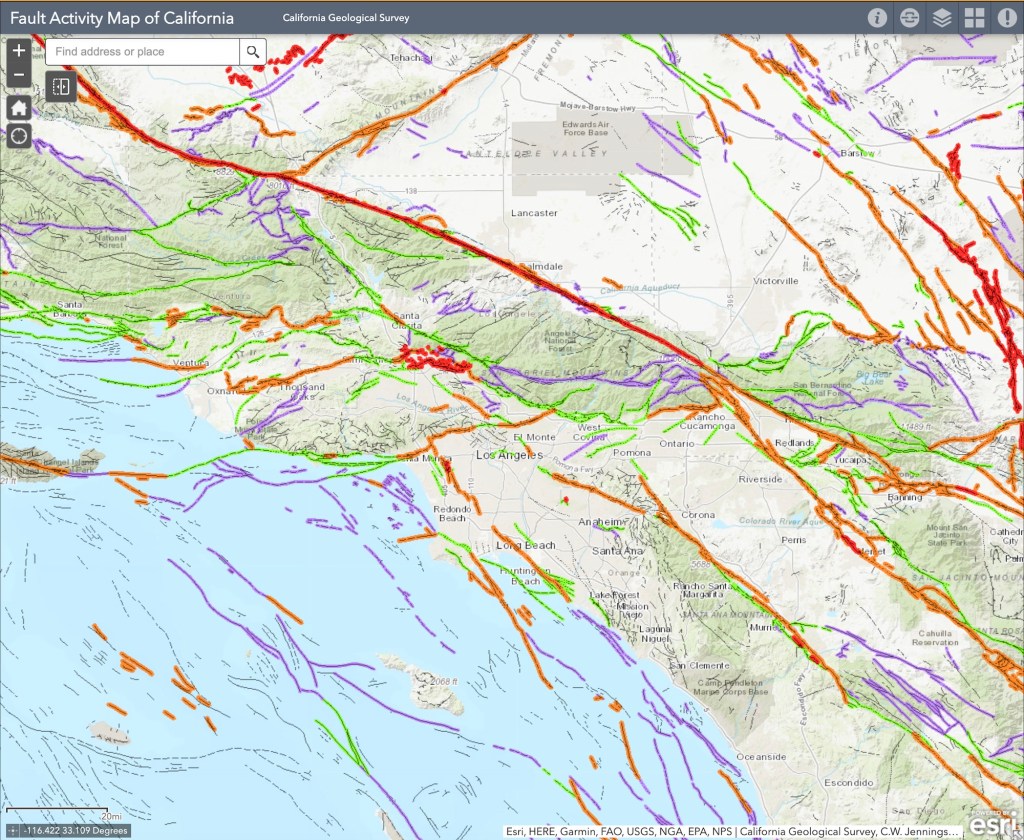
The area around the Salton Sea is located in a techtonically active region, with the San Andreas Fault running directly through it. The San Andreas Fault is a major plate boundary, where the Pacific Plate is moving north relative to the North American Plate (see our story about how fast it’s moving here). As pretty much every Californian knows, the legendary fault is responsible for the earthquakes and other tectonic activity across much of California.
If you look at a map of the area, you can see how the low lying southern portion of the Salton Sea basin goes directly into the Gulf of California. Over millions of years, the desert basin has been flooded numerous times throughout history by what is now the Gulf of California. As the fault system cuts through the region, the Pacific Plate is slowly sliding northwest, gradually pulling the Baja Peninsula away from mainland Mexico. Over millions of years, this tectonic motion is stretching and thinning the crust beneath the Imperial Valley and Salton Basin. If the process continues, geologists believe the area could eventually flood again, forming a vast inland sea, perhaps even making an island out of what is today Baja California. (We wrote about this earlier.)

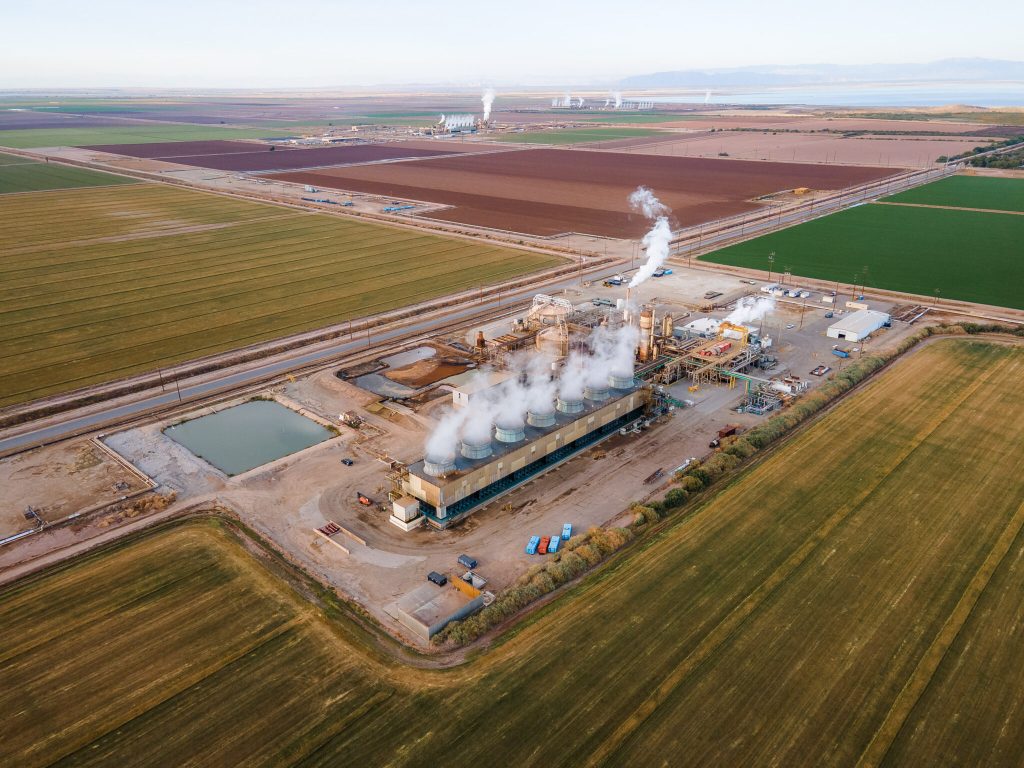
Yet even as the land shifts beneath it, the Salton Sea’s future may be shaped not just by geology, but by energy. Despite the ongoing controversy over the evaporating water body, the Salton Sea may play a crucial role in California’s renewable energy future. The region sits atop the Imperial Valley’s geothermal hotspot, where underground heat from all that tectonic activity creates ideal conditions for producing clean, reliable energy. Already home to one of the largest geothermal fields in the country, the area is now gaining attention for something even more strategic: lithium.

(Credit: Courtesy Lawrence Berkeley National Lab)
Beneath the surface, the hot, mineral-rich brine used in geothermal energy production contains high concentrations of lithium, a critical component in electric vehicle batteries. Known as “Lithium Valley,” the Salton Sea region has become the focus of several ambitious extraction projects aiming to tap into this resource without the large environmental footprint of traditional lithium mining. Gov. Gavin Newsom called the area is “the Saudi Arabia of lithium.” Even the Los Angeles Times has weighed in, claiming that “California’s Imperial Valley will be a major player in the clean energy transition.”
Companies like Controlled Thermal Resources (CTR) and EnergySource are developing direct lithium extraction (DLE) technologies that pull lithium from brine as part of their geothermal operations. The promise is a closed-loop system that produces both renewable energy and battery-grade lithium on the same site. If it proves viable, the Salton Sea could significantly reduce U.S. dependence on foreign lithium and cement California’s role in the global shift to clean energy. That’s a big if…and one we’ll be exploring in depth in future articles.
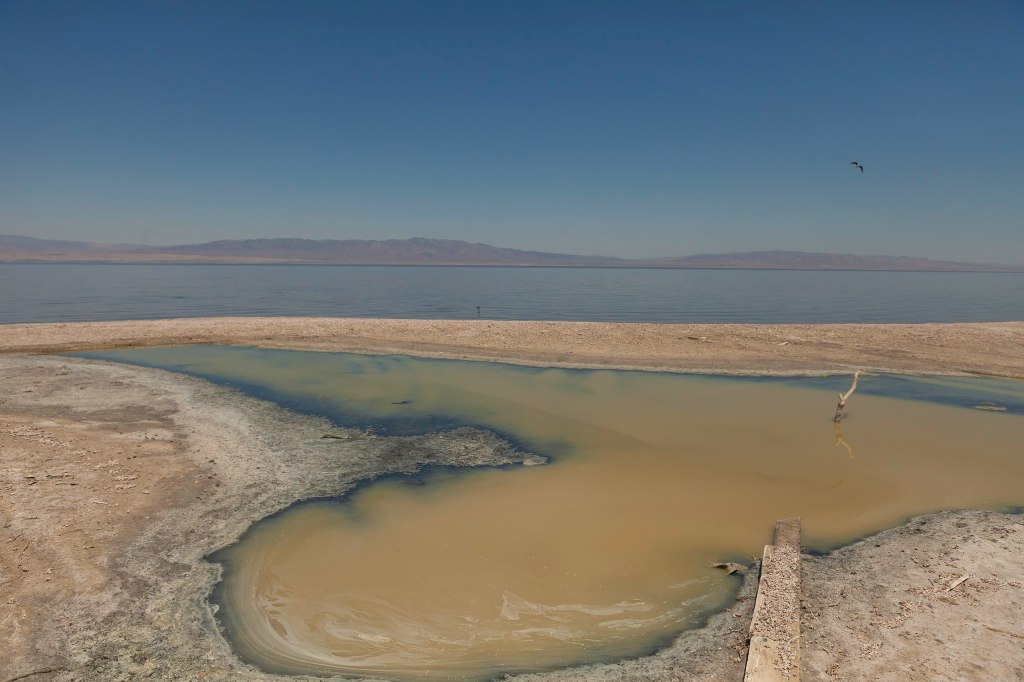

Such projects could also potentially provide significant economic investment in the region and help power California’s green energy ambitions. So for a place that looks kind of wrecked and desolate, there actually a lot going on. We promise to keep an eye on what happens. Stay tuned.